India’s manufacturing landscape is undergoing a dramatic transformation. For decades, metropolitan cities like Mumbai, Chennai, and Pune dominated industrial activity.
Today, a new pattern is emerging. Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities are becoming the powerhouses of manufacturing growth and talent acquisition.
This shift isn’t accidental. It’s driven by a convergence of factors: prohibitive operational costs in metros, government policy incentives, improved infrastructure in smaller cities, and perhaps most critically, access to abundant, stable talent.
As India positions itself as a global manufacturing hub, the geography of manufacturing hiring in India is being redrawn, with Tier-2 cities manufacturing jobs and Tier-3 cities hiring leading the charge.
Why Manufacturing Is Moving Beyond Metro Cities?
The decentralization of India’s manufacturing sector reflects both push and pull factors. Metro cities, while offering established ecosystems, come with significant challenges that are prompting manufacturers to look elsewhere.
High Operational Costs and Attrition: Real estate prices, wage inflation, and intense competition for talent have made metros increasingly expensive. Attrition rates in manufacturing roles often exceed 30-40% annually in major cities, disrupting production cycles and inflating hiring costs.
Government Policy Push: India Decoding Jobs Report 2026 highlights that initiatives like Make in India, Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes, and the development of industrial corridors have strategically targeted non-metro regions. State governments are offering attractive land packages, tax incentives, and infrastructure support to establish manufacturing clusters in emerging cities.
Infrastructure Transformation: The infrastructure gap that once separated Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities from metros has narrowed considerably. Improved highways, dedicated freight corridors, better connectivity through airports and rail networks, and reliable power supply have made these locations viable for sophisticated manufacturing operations.
Tier-2 & Tier-3 Cities are the New Manufacturing Talent Hubs
India Decoding Jobs 2026 highlights that manufacturing hiring in India is rapidly decentralizing, with only 35% of hiring now concentrated in Tier-1 cities, while Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities account for nearly 65% of new manufacturing hires.
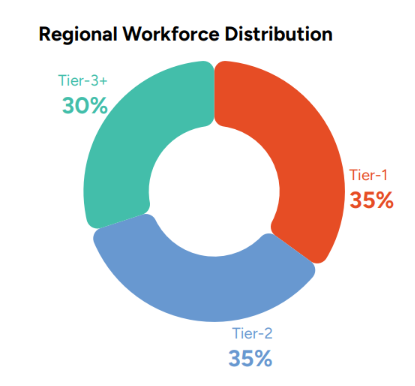
Alt: Regional workforce distribution in Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities
This shift is driven by rising metro costs, government incentives, and the growth of satellite industrial clusters. These cities offer access to stable, skilled engineering and vocational talent, lower attrition, and proximity to production hubs- making them critical to India’s next phase of manufacturing-led growth.
These emerging cities offer unique talent benefits that are reshaping hiring strategies.
Proximity to Raw Materials and Supplier Ecosystems: Many Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities have developed around specific industries- textiles in Tirupur, automotive in Hosur, engineering goods in Coimbatore. This creates natural talent pools with industry-specific skills and understanding.
Strong Educational Pipelines: These cities host numerous Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs), polytechnics, and engineering colleges that produce job-ready graduates. Unlike metros where graduates often pursue software jobs or further education, students in these regions are more inclined toward manufacturing careers, creating a consistent talent pipeline.
Lower Wage Inflation and Higher Stability: Salary expectations are 20-35% lower than metros for comparable roles, but more importantly, workforce stability is significantly higher. Employees in these cities typically have stronger local roots, family ties, and community connections, translating to retention rates that often exceed 80% compared to 60-70% in metros.
Manufacturing Roles in High Demand Across Tier-2 & Tier-3 Cities
Manufacturing roles in Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities are witnessing strong demand as companies expand plants, diversify supply chains, and tap into cost-efficient, skilled local talent. These locations are becoming critical for shop-floor excellence, quality control, automation, and supply chain stability, creating sustained hiring momentum across core manufacturing functions.
The manufacturing hiring boom in these cities spans the entire operational spectrum.
1. Production & Plant Operations Roles
Production engineers, shift supervisors, and plant managers form the backbone of manufacturing operations. These roles require hands-on experience with production processes, quality standards, and team management. The demand is particularly high for professionals who can handle multi-shift operations and scale production rapidly.
2. Quality & Process Excellence Roles
As manufacturers compete globally, quality cannot be compromised. Quality engineers, Six Sigma professionals, and process improvement experts are critical for maintaining certifications, reducing defects, and implementing lean manufacturing principles. These roles often require formal training and certification, making experienced candidates highly sought after.
3. Maintenance & Reliability Engineers
With increasing automation and sophisticated machinery, maintenance expertise has become crucial. Electrical maintenance engineers, mechanical specialists, and automation technicians who can minimize downtime and ensure equipment reliability are in constant demand. Preventive maintenance and reliability engineering skills are particularly valued.
4. Supply Chain & Procurement Professionals
Manufacturing success depends on seamless supply chains. Roles in production planning, materials sourcing, logistics coordination, and vendor management are expanding rapidly. Professionals who understand regional supplier networks and can optimize local procurement have a distinct advantage.
5. EHS & Compliance Specialists
Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) officers, sustainability coordinators, and regulatory compliance experts are essential. As manufacturing facilities scale and regulatory requirements tighten, these professionals ensure operations remain compliant and workers stay safe.
Key Tier-2 & Tier-3 Cities Driving Manufacturing Hiring
The manufacturing sector shows a positive hiring intent of 10% for FY 27, reflecting a steady increase. This growth is driven by rising production demand, industrial recovery, and expansion of manufacturing operations across core industries.
Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities are emerging as major manufacturing hiring hubs due to industrial corridor development, lower operating costs, and access to locally skilled talent.
Cities such as Coimbatore, Indore, Surat, Vadodara, Nagpur, Ludhiana, Hosur, Tiruppur, Rajkot, and Aurangabad are attracting large-scale investments in automotive, textiles, electronics, chemicals, and engineering, driving consistent demand for production, quality, maintenance, and supply chain professionals.
Check out the details below-
Tamil Nadu: Coimbatore has become synonymous with pump and motor manufacturing, while Hosur dominates automotive components. Salem is known for steel and textiles, and Tiruppur remains India’s knitwear capital. The state’s focus on industrial development and skilled workforce makes it a top destination.
Maharashtra: Nashik’s automotive and wine industries, Aurangabad’s manufacturing base anchored by major automotive players, and Kolhapur’s engineering goods sector create diverse opportunities. These cities benefit from proximity to Mumbai’s markets while offering significantly lower costs.
Gujarat: Ahmedabad, Vadodara, Rajkot, and Surat have established themselves as industrial powerhouses. The state’s business-friendly policies, strong entrepreneurial culture, and well-developed infrastructure support everything from chemicals and pharmaceuticals to textiles and engineering goods.
Karnataka: Beyond Bengaluru, cities like Hubli-Dharwad, Belagavi, and Tumakuru are emerging as manufacturing centers. The state government’s push to develop industrial corridors and attract investments has created substantial hiring activity, particularly in automotive and aerospace components.
North India: Ludhiana’s bicycle and auto parts industries, Panipat’s textiles, and the industrial zones of Bhiwadi and Neemrana (benefiting from NCR proximity) offer diverse manufacturing opportunities. These locations attract both domestic and international manufacturers seeking northern India bases.
Why Employers Prefer Hiring from Tier-2 & Tier-3 Cities
The preference for these locations extends beyond operational cost savings to strategic talent advantages.
Better Talent Retention and Lower Attrition: The stability factor cannot be overstated. Employees in these cities view manufacturing jobs as solid career options rather than stepping stones. Family proximity, established social networks, and lower job-hopping culture contribute to retention rates that significantly reduce hiring and training costs.
Faster Ramp-up and Training Adaptability: Candidates from these regions often bring practical, hands-on orientation and a willingness to learn. They’re generally more adaptable to shift work, shop floor environments, and the physical demands of manufacturing roles. Training programs see higher completion rates and faster skill acquisition.
Strong Local Loyalty and Workforce Continuity: Manufacturing operations benefit enormously from experienced teams that understand plant-specific processes and equipment. In Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities, building such teams is more feasible. Multi-generational employment within the same company isn’t uncommon, creating knowledge continuity that’s invaluable for complex operations.
Recruitment Challenges in Tier-2 & Tier-3 Manufacturing Locations
Companies often face recruitment challenges in Tier–2 and Tier-3 hiring.
One of the challenges is the skill readiness gaps as advanced automation, quality, and digital manufacturing skills are still developing locally. Leadership and specialist talent availability is limited, requiring relocation or accelerated upskilling.
Additionally, employer branding is weaker compared to metro-based firms, making it harder to attract experienced professionals.
Infrastructure gaps, slower hiring processes, and limited exposure to global manufacturing practices further add to recruitment complexity.
Limited Access to Niche or Advanced Skills
While basic manufacturing skills are abundant, specialized capabilities- advanced automation programming, Industry 4.0 technologies, specialized quality systems can be scarce. Companies often need to import this expertise or invest heavily in upskilling local talent.
Gaps in Leadership and Plant Management Talent
Experienced plant managers, operations heads, and senior leadership with multi-site experience are harder to find. Many talented mid-level professionals are reluctant to relocate from metros to smaller cities, creating leadership pipeline challenges.
Need for Localized Hiring Expertise and Networks
Successful hiring requires understanding local labor markets, educational institutions, wage benchmarks, and cultural nuances. Generic hiring approaches often fail. Partnerships with local placement agencies, ITIs, and community networks become essential for consistent talent access.
Smart Hiring Strategies for Manufacturing in Emerging Cities
To succeed in Tier-2 and Tier-3 manufacturing hubs, companies must shift from reactive hiring to ecosystem-driven talent strategies. Employers that invest early in local capability building gain long-term cost and retention advantages. Effective hiring in emerging cities blends workforce planning, skilling partnerships, and localized talent branding.
1. Build Local Talent Pipelines Early
Engaging with regional ITIs, polytechnics, and engineering colleges through campus recruitment creates dedicated talent channels. Companies that establish early relationships through guest lectures, facility tours, projects, and internships build brand recognition and first access to graduating talent.
This approach reduces dependency on scarce experienced hires and allows companies to shape talent to their specific needs.
2. Invest in Skill Development & Apprenticeships
Industry-academia collaboration models are proving highly effective. By working with educational institutions to align curricula with industry needs, companies ensure graduates possess relevant skills.
Structured apprenticeship programs that combine classroom learning with on-the-job training create ready-to-deploy talent while demonstrating commitment to workforce development.
3. Hire for Learnability, Not Just Experience
Given skill scarcity in certain areas, prioritizing candidates’ ability and willingness to learn often yields better outcomes than holding out for perfect experience matches.
Robust training programs, mentorship systems, and clear career progression paths can transform motivated learners into high-performing team members. This approach expands the talent pool significantly.
4. Strengthen Employer Branding Locally
In smaller cities, employer reputation spreads through community networks. Companies that invest in being good corporate citizens supporting local development initiatives, maintaining strong safety records, treating employees well- find hiring becomes progressively easier as positive word-of-mouth builds.
Local marketing through regional job fairs, community engagement, and transparent communication about career opportunities strengthens brand perception.
The Role of RPO in Tier-2 & Tier-3 Manufacturing Hiring
Recruitment Process Outsourcing (RPO) providers with manufacturing expertise offer distinct advantages in these markets, particularly for companies scaling rapidly or entering new geographies.
Hyperlocal Sourcing and On-Ground Networks: Effective RPO partners maintain physical presence and deep networks in these cities. They understand local labor markets, have relationships with educational institutions, and know where to find niche talent. This local intelligence is difficult for companies to develop independently, especially when establishing new facilities.
Volume Hiring at Speed Without Quality Compromise: When a new plant needs to hire 500+ workers across multiple roles within tight timelines, specialized RPO for manufacturing becomes invaluable. These providers can mobilize resources, conduct mass assessments, and onboard at scale while maintaining quality standards and cultural fit.
Compliance, Wage Benchmarking, and Workforce Planning: RPO partners help navigate complex compliance requirements that vary by state and location. They provide market intelligence on competitive wages, benefits expectations, and hiring practices. Strategic RPO engagement includes workforce planning- anticipating talent needs based on production scaling, helping structure roles optimally, and identifying potential talent shortages before they become critical.
Manufacturing hiring solutions that combine RPO capabilities with industry understanding enable manufacturers to focus on operations while ensuring talent acquisition keeps pace with growth.
Future Outlook: Tier-2 & Tier-3 Cities as Manufacturing Growth Engines
The trajectory for manufacturing in these cities points toward sustained growth with evolving skill requirements.
Smart Factories and Automation-Led Hiring: As Industry 4.0 technologies penetrate manufacturing, the skill profile is changing. Tomorrow’s shop floor workers will need digital literacy, data interpretation skills, and comfort with automated systems. Forward-looking employers are already upskilling current workforces and adjusting hiring criteria to emphasize technology adaptability alongside traditional manufacturing skills.
Rising Demand for Digitally Skilled Shopfloor Talent: The convergence of IT and operations technology (OT) creates new hybrid roles- maintenance technicians who can troubleshoot PLC programming, quality engineers who analyze statistical data using software tools, production supervisors who monitor real-time digital dashboards. Educational institutions in these cities are beginning to adapt curricula, but employer-led training will remain crucial.
Leadership Development in Emerging Industrial Clusters: As manufacturing concentrations in these cities mature, developing local leadership becomes both possible and necessary. Companies that invest in leadership development programs, create clear progression paths, and promote from within will build competitive advantages. This approach also addresses the challenge of attracting senior talent from metros by growing it organically.
Wrapping Up
India’s manufacturing ambition- becoming a $1 trillion manufacturing economy won’t be achieved solely through metros. The real growth story is being written in cities like Coimbatore, Nashik, Rajkot, and dozens of others across the country.
For manufacturers, this geographic shift represents both opportunity and imperative. Those who recognize Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities not as compromises but as strategic advantages will build more resilient, cost-effective operations.
Success requires moving beyond traditional hiring approaches to embrace localized strategies including early engagement with regional educational ecosystems, investment in training and skill development infrastructure, partnerships with specialized recruitment providers who understand these markets, and commitment to being strong local employers that contribute to community development.
Manufacturing growth is becoming decentralized, and this trend will only accelerate. Companies that establish themselves as employers of choice in these emerging hubs today will reap compounding benefits in talent access, operational stability, and cost competitiveness for years to come.
FAQs
Why are Tier-2 cities preferred for manufacturing hiring?
These cities offer an optimal balance of cost efficiency, talent availability, and operational stability. Lower wage inflation, higher retention rates, access to industry-focused educational institutions, and improved infrastructure make them attractive alternatives to metros. Government incentives and proximity to raw materials further enhance their appeal.
Which manufacturing roles are most in demand?
Production engineers and operators, quality assurance professionals, maintenance technicians (especially electrical and automation specialists), supply chain coordinators, and EHS officers are consistently in high demand. As facilities automate, roles requiring both mechanical understanding and digital skills are increasingly sought after.
How do companies manage skill gaps in smaller cities?
Successful companies adopt multi-pronged approaches including structured training programs and partnerships with local educational institutions to shape curricula. They hire for attitude and learnability rather than perfect experience matches, establish apprenticeship programs that develop talent from the ground up, and bring in specialized expertise from metros for initial setup and knowledge transfer while developing local capabilities over time.
Is RPO effective for regional manufacturing hiring?
Yes, particularly RPO providers with manufacturing specialization and local presence. They navigate the unique challenges of regional hiring including accessing hyperlocal talent networks that generic job portals miss, understanding regional compliance and labor law variations, providing market intelligence on competitive compensation, and managing volume hiring during plant ramp-ups. The effectiveness depends on the provider’s actual ground presence and manufacturing industry understanding rather than just process capability.
What are the long-term benefits of non-metro hiring?
Beyond immediate cost savings, long-term advantages include sustainable talent pipelines through relationships with local institutions, workforce stability that enables operational excellence and knowledge continuity, community integration that strengthens employer brand and eases future hiring, and scalability potential as these locations continue developing infrastructure and talent ecosystems. Companies establishing presence now position themselves advantageously as these cities mature into major manufacturing hubs.
Looking to Scale Manufacturing Teams Across Tier-2 & Tier-3 Cities?
Taggd’s RPO-led manufacturing hiring solutions help you access regional talent faster, reduce attrition, and build resilient workforces. With deep local networks, manufacturing expertise, and proven processes for volume hiring, we enable your manufacturing expansion across India’s emerging industrial hubs.
Contact us to discuss your manufacturing talent strategy.








