India’s automobile sector is entering its most transformative growth phase driven by electrification, localisation, and global demand. According to Taggd’s India Decoding Jobs 2026, the market projected to reach $300 billion by 2026.
India has strengthened its position as a global manufacturing powerhouse: the world’s largest three-wheeler producer, among the top two for two-wheelers, and ranking within the top four in passenger vehicles and top five in commercial vehicles.
The industry is not just scaling in output- it is evolving in capability. By FY28, India is expected to invest $7 billion in component localisation, including electric motors and automatic transmissions, reducing import dependency and catalysing domestic manufacturing.
This shift is supported by cost-efficient skilled talent, robust R&D ecosystems, and abundant steel production, positioning the automotive sector for accelerated innovation and employment expansion.
A major driver of future growth is electric mobility, projected to generate nearly 5 crore jobs by 2030, spanning vehicle design, battery engineering, EV manufacturing, charging infrastructure, aftermarket support, and green logistics.
In FY25 alone, India recorded over 1.96 crore two-wheeler sales, 43 lakh passenger vehicles, 9.5 lakh commercial vehicles, and 7.4 lakh three-wheelers, while total vehicle production crossed 3.1 crore units. Electric vehicle sales surged 45% YoY in Q1 2025, and India aims for 30% EV penetration by 2030, strengthening future employment pipelines across the auto and EV value chain.
As we move toward 2026, hiring trends in the automobile industry are expected to sharpen around EV engineering, advanced mobility manufacturing, autonomous systems, supply-chain digitisation, and sustainable production models. This blog deep-dives into what’s next — the roles, skill shifts, and workforce demand that will define India’s automotive talent landscape.
Top Automobile Industry Hiring Trends in India
The Indian automobile sector is undergoing a rapid transformation and hiring trends for 2026 are increasingly shaped by electrification, digitalisation, and advanced manufacturing technologies.
Companies are gearing up to meet both production and innovation demands, making talent acquisition a strategic priority.
Accelerating EV Adoption
The shift toward sustainable mobility is driving a surge in electric vehicle (EV) demand. By 2030, EVs are expected to account for 30% of India’s new vehicle sales, with the market growing at an impressive 45–50% year-on-year.

This rapid expansion is fuelling demand for professionals skilled in EV design, battery technology, powertrain engineering, and EV manufacturing operations.
Digitalisation & Industry 4.0 Implementation
Automakers are embracing Industry 4.0 technologies to enhance manufacturing efficiency, predictive maintenance, and innovation. Government-supported initiatives have completed digital maturity assessments for over 100 automotive companies, identifying key areas for improvement.
This trend is boosting hiring for automation engineers, IoT specialists, and digital manufacturing experts, as companies integrate smart factories and data-driven production models.
Talent Upskilling & Skill Demand
Rapid technological shifts are creating an urgent need for EV-skilled and tech-savvy talent. Estimates suggest India will require 100,000–200,000 EV professionals by 2030, including engineers, technicians, and software specialists.
In response, companies and government programs are investing heavily in training, apprenticeships, and reskilling initiatives to bridge the talent gap.
Connected & Autonomous Vehicle Technologies
The industry’s focus on connected vehicles and autonomous driving is reshaping workforce requirements. Features such as advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and vehicle connectivity demand software developers, data analysts, cybersecurity experts, and AI engineers, positioning tech and mobility skills at the forefront of hiring priorities.
Automation Driving Women Recruitment
Automation in manufacturing is not only improving efficiency but also creating inclusive work environments.
Auto companies that have adopted automated processes are increasingly hiring women workforce, expanding participation beyond the traditional 15–20%, and encouraging gender diversity across shop floors and technical roles.
Sustainability & Green Manufacturing
Automakers are investing in carbon-neutral factories, material recycling, and energy-efficient production technologies. This shift creates demand for professionals skilled in sustainability, robotics, battery chemistry, data-driven manufacturing, and ESG compliance, making green skills a key factor in future hiring strategies.
For HR leaders and CHROs, these trends underline the importance of strategic workforce planning, large-scale hiring, and focused reskilling programs. The roles in engineering, digital, analytics, and field service are expected to see the highest demand, shaping the automotive talent landscape for 2026 and beyond.
Explore key details further in India Decoding Jobs Report 2026.
Region-Wise Automobile Industry Growth & Key Employers in India
India’s automobile industry is rapidly evolving, driven by strong investments in electric vehicles (EVs), export growth, and government initiatives supporting clean mobility infrastructure. By 2030, the sector is expected to become one of the largest globally, with manufacturing hubs expanding across North, South, West, and East India.
Below is a region-wise breakdown of key cities, major companies, projects, and focus areas.
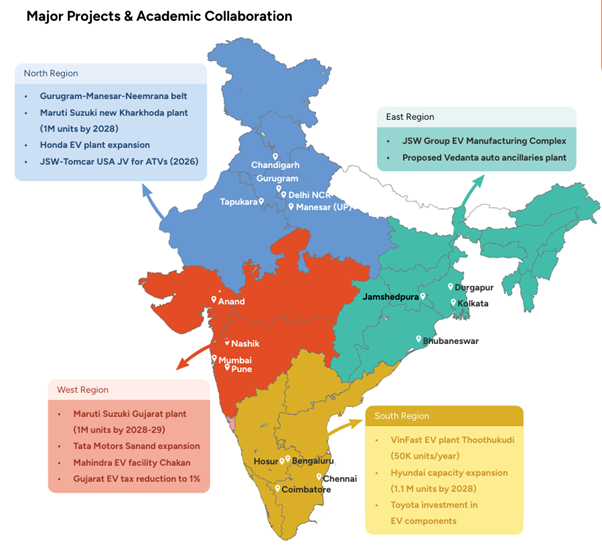
| Region | Key Cities/Nodes | Public & Private Companies | Major Projects & Joint Ventures | Main Focus Areas |
| North | Delhi NCR (Gurgaon, Manesar, Kharkhoda), Chandigarh, Tapukara (Rajasthan) | Maruti Suzuki, Honda, Hero MotoCorp, Bajaj Auto, TVS Motor, Ashok Leyland, JSW Sarbloh Motors | • Maruti Suzuki Kharkhoda plant (1M units by 2028) • Honda EV plant expansion • JSW-Tomcar USA JV for ATVs (2026) | ICE vehicle manufacturing, EV transition, SUV production, all-terrain vehicles, automotive components, export hub development |
| South | Chennai, Bengaluru, Hosur, Thoothukudi, Ranipet, Sriperumbudur, Coimbatore | Hyundai, Ford, Tata Motors, Toyota, Renault-Nissan, BMW, VinFast, Mahindra & Mahindra, Isuzu, Kia | • VinFast EV plant Thoothukudi (50K units/year) • Hyundai capacity expansion (1.1M units by 2028) • Toyota investment in EV components | EV manufacturing, automotive exports, all-electric clusters, premium vehicle production, battery manufacturing |
| West | Pune (Chakan, Aurangabad), Mumbai, Sanand (Gujarat), Nashik, Halol | Bajaj Auto, Mahindra & Mahindra, Tata Motors, Volkswagen, Audi, Škoda, Force Motors, MG Motors, Maruti Suzuki | • Maruti Suzuki Gujarat plant (1M units by 2028–29) • Tata Motors Sanand expansion • Mahindra EV facility Chakan • Gujarat EV tax reduction to 1% | EV manufacturing, automotive components, SUV production, premium vehicles, export-oriented manufacturing, battery technology |
| East | Kolkata, Jamshedpur, Bhubaneswar, Durgapur | Hindustan Motors, Tata Motors, Heavy Engineering Corporation, Tata Hitachi Construction | • JSW Group EV Manufacturing Complex • Proposed Vedanta auto ancillaries’ plant | Commercial vehicle manufacturing, automotive components, heavy engineering, industrial vehicles, emerging EV adoption |
Key Insights as highlighted in India Decoding Jobs 2026- Fourth and Forward – Fuelled by Talent:
- North India is emerging as a hub for ICE vehicles, SUVs, all-terrain vehicles, and automotive exports.
- South India is focused on EV production, battery manufacturing, and premium vehicles.
- West India is expanding its EV and SUV manufacturing footprint, supported by tax incentives and private-sector investments.
- East India is growing in commercial vehicles, industrial vehicles, and EV adoption, with investments in ancillary and heavy engineering sectors.
With rising demand, technological advancements, and sustainability initiatives, India’s automobile sector is poised to triple output and lead in EV adoption by 2030, creating massive employment opportunities across the country.
Key Challenges Facing India’s Automotive Industry
India’s automobile sector is undergoing a rapid technological transformation, with electric vehicles (EVs), autonomous systems, connected technologies, and digital manufacturing reshaping the industry.
While these changes open up significant growth opportunities, they also create pressing challenges in talent acquisition, skill development, and workforce management. Understanding these challenges is crucial for HR leaders, CHROs, and automotive employers aiming to stay competitive and future ready.
Electric Vehicle Technology Gap
The shift toward EVs has highlighted a severe skills gap in high-tech roles, including battery engineering, automation, data analytics, and EV software development. While India produces a large number of engineering graduates annually, only around 55% are considered employable for these specialized roles.
As a result, the industry faces an estimated 80% skills gap, making it difficult to scale EV production and innovation.
Rising Demand for Software & Digital Engineering Talent
With the rise of software-defined vehicles (SDVs), automotive companies now require expertise in embedded systems, AI, cybersecurity, and vehicle connectivity.
Currently, there are 4.3 vacancies per 100 employees, reflecting acute talent shortages. Less than half of Indian OEMs and suppliers are able to scale digital initiatives effectively in 2025. Upskilling programs such as the Accenture–IIT Madras partnership aim to bridge this gap, but rapid workforce development remains a top priority.
Digital capabilities are expected to account for 40% of sector revenue by 2040, highlighting the critical need for skilled software and analytics professionals today.
Diversity and Inclusion Challenges
Women are significantly underrepresented in India’s automotive workforce, making up only 16% of employees in NSE-listed firms and just 20% of leadership roles. This lack of diversity impacts innovation, as studies show that diverse teams deliver 15–20% higher revenues than male-dominated teams.
Addressing gender imbalance is therefore key to fostering creativity, driving business performance, and strengthening the talent pipeline.
Aging Workforce
Nearly half of production workers are over 40, and many experienced professionals are approaching retirement. At the same time, younger talent is increasingly drawn to sectors such as technology, healthcare, and finance, leaving a shrinking pool for critical manufacturing, repair, and maintenance roles.
Companies must plan proactively to transfer knowledge, retain experienced staff, and attract younger talent to sustain operations.
Talent Retention Challenges
With high competition for skilled professionals, especially in core technical and digital roles, retaining talent has become difficult. Employers face challenges such as limited career progression, competitive poaching, and compensation pressures, with 60% of automotive companies reporting difficulty recruiting and retaining critical staff.
Building robust employee engagement, upskilling, and incentive programs is essential to reduce attrition and maintain operational efficiency.
Global Automotive Trends 2026–2030
The global automotive industry is set for significant transformation over the next decade. By 2030, worldwide vehicle production is projected to exceed 96 million units, though growth is uneven across regions.
China and the broader Global South are leading production expansion, while Europe and North America remain below pre-2020 levels, with projected outputs of 16–17 million and 15–16 million vehicles, respectively.
This shift is driving automakers to focus expansion, hiring, and investment in fast-growing markets while maintaining cautious operations in Western regions.
Electric Vehicle (EV) Adoption & Hybrid Market Growth
Battery electric vehicle (BEV) adoption is growing globally, yet more slowly than anticipated in Europe and North America due to subsidy cuts and high costs.
Consequently, hybrid vehicles are gaining traction to fill the gap. By 2030, BEVs are expected to account for 41% of global light-vehicle sales, with Europe and China potentially reaching 50–55% penetration, while North America lags at 20–30%. This dual demand necessitates talent retention in internal combustion and hybrid technologies alongside expansion of electric drivetrain teams.
Geopolitical Factors Influencing Hiring
Trade tensions and localisation policies are reshaping automotive workforce strategies. Nearly 91% of employers cite trade uncertainty as a key concern. While some companies plan to maintain staff levels, others are cautiously hiring, particularly in EV production, gigafactories, assembly plants, and supply chains. HR and talent teams must balance workforce stability with the need for new EV and digital capabilities.
Changing Skill Profiles & Talent Demand
The rise of electrification, autonomy, and connectivity is driving demand for hybrid skill sets. Employers now seek professionals who combine technical expertise with soft skills like adaptability, problem-solving, and teamwork. Key areas of talent demand include:
- Battery design engineers and assembly technicians
- High-voltage safety specialists and recycling/reuse engineers
- Electric drivetrain engineers (e-motors, gear reducers, power control units)
- Data analysts, machine learning engineers, and software developers for autonomous and connected vehicles
For example, the U.S. automotive sector projects a 26% increase in software developer jobs by 2031, driven by the growth of data-driven vehicles and predictive maintenance technologies.
Get the full projection report in India Decoding Jobs 2026– Download the report for CHRO-grade insights.
Indian Automotive Landscape
India’s automotive sector continues to be a bellwether for economic growth and technological adoption. With an EV market projected at $206 billion by 2030, India requires an estimated $180 billion in vehicle manufacturing and charging infrastructure investment.
The EV finance sector is expected to grow to $50 billion in the same period. Government initiatives like PLI, FAME II, PM E-Drive, and ACC Battery Storage are fueling growth, creating thousands of jobs across manufacturing, R&D, and supply chain functions.
Major Manufacturing & Expansion Projects
- Maruti Suzuki: $864 million investment for a third car plant in Haryana, capacity reaching 7,50,000 units/year by 2029.
- Tata Motors: Gujarat EV plant expansion and EV model launches.
- Mahindra & Mahindra: $1.43 billion investment in EV subsidiary with new electric SUV models.
- Honda: Dedicated electric motorcycle plant in Karnataka by 2028.
Women & Workforce Diversity in India
India’s automotive sector is seeing increased participation of women engineers and technicians. Examples include:
- Tata Motors: 6,500+ women shop-floor technicians, with an all-women team of 3,000 assembling SUVs.
- Hero MotoCorp: Women-led assembly lines aiming for 30% female workforce by 2030.
- MG Motor: Over one-third of workforce female.
Supportive measures include safe transportation, parental leave, on-site crèches, and targeted recruitment/training programs.
Skill Development & Future-Ready Talent
Collaboration between industry, academia, and government is essential to meet future skill demands:
- ASDC programs: Vocational training in EV maintenance, battery assembly, and automotive electronics.
- State initiatives: EV-focused training in Tamil Nadu and Maharashtra.
- Corporate programs: Maruti Suzuki and Toyota expanding institutes for skilled shop-floor workers and supervisors; sponsorship for advanced degrees in electric mobility and autonomous systems.
These efforts aim to prepare India’s workforce to design, manufacture, and maintain next-generation vehicles, positioning the country as a global leader in EV and advanced automotive technology by 2030.
Future Automotive Hiring Trends
As per India Decoding Jobs 2026, the automotive hiring landscape is entering one of its most dynamic phases, driven by electrification, automation, and the shift toward software-defined vehicles. Over FY26–27, India will witness strong job creation across EV manufacturing, battery technology, autonomous systems, and automotive software.
The result is not only more employment opportunities but also sustained compensation growth as companies compete to secure niche, future-ready talent.
Salary Growth Will Outpace India Inc.
- The automotive sector is expected to lead salary growth for the fifth consecutive year, with an average projected hike of 10.1% in FY26, significantly higher than the India Inc average of 8.8%.
- Leadership, R&D, EV engineering, and software roles are likely to see the steepest pay increases as demand for specialised skills intensifies.
Demand for Software and AI Talent Will Surge
- The automotive software market is projected to hit $43 billion by 2027, creating unprecedented demand for:
- AI & ML engineers
- Automotive software developers
- Embedded systems engineers
- Data scientists for vehicle analytics
Software-defined vehicles (SDVs) will require continuous OTA updates, predictive decision engines, and real-time data processing, making automotive tech talent one of the most aggressively hired skill pools of FY26–27.
Autonomous Systems Will Create New Engineering Roles
- India’s autonomous vehicle market is expected to touch $23.3 billion by 2033, at a CAGR of 24.3%.
- Hiring demand will intensify for:
- ADAS engineers
- Computer vision specialists
- LiDAR/RADAR integration engineers
- Sensor fusion architects
With OEMs and deep-tech startups expanding test tracks and simulation labs, talent for autonomy R&D will be one of the fastest-growing recruitment segments.
Automotive Cybersecurity Becomes Non-Negotiable
- The global automotive cybersecurity market is set to reach $31.34 billion by 2031 at nearly 19% CAGR.
- Demand is rising for experts in:
- Vehicle intrusion detection
- Secure ECU/communication protocols
- ISO 21434 & UNECE R155 compliance
- Encryption for connected vehicle platforms
Every connected car adds millions of lines of code, making cybersecurity core infrastructure rather than a support function.
Large-Scale Reskilling Will Reshape the Workforce
- Only 43% of technical competencies overlap between ICE and EV roles, highlighting a major skill shift.
- Nearly 27% of automotive skills require structured reskilling across:
- Battery & energy storage systems
- High-voltage architecture
- Power electronics
- EV diagnostics & testing
Upskilling and cross-domain learning will become the foundation of workforce readiness.
Wrapping Up
The global and Indian automotive industries are entering a defining decade, marked by electrification, software-defined mobility, connected ecosystems, and advanced manufacturing.
Demand for skilled talent is accelerating, especially in EV engineering, battery innovation, autonomous systems, data science, and cybersecurity. India stands at a strategic advantage with strong policy support, rising domestic consumption, and large-scale OEM investments.
Going forward, the winners in the automotive revolution will be the companies that hire fast, build future-ready skills, and adapt to new technology cycles. With gigafactories coming online, OEM expansions underway, and a surge in tech-driven roles, FY26–27 will reshape the automotive talent landscape, creating opportunities for millions and pushing the industry into its most transformative era yet.
FAQs
What is driving automotive hiring growth in FY26–27?
Hiring growth is primarily driven by EV adoption, autonomous vehicle development, battery manufacturing, and the rise of software-defined mobility. Companies need skilled engineers and digital talent to support this transition.
Which skills will be in highest demand in the automotive industry by 2027?
Battery engineering, EV powertrain design, ADAS development, machine learning, embedded systems, and cybersecurity will be among the most sought-after skills.
What is the outlook for automotive software jobs?
The automotive software market is projected to reach $43 billion by 2027, leading to a surge in roles for software developers, AI engineers, and data scientists.
How is the shift to electric vehicles impacting automotive jobs?
Only 43% of ICE and EV skills overlap, meaning EV growth is creating new jobs and requiring large-scale reskilling in power electronics, high-voltage systems, battery assembly, and energy storage.
Will salary growth remain strong in the automotive sector?
Yes. The industry is projected to see an average salary hike of 10.1% in FY26, the fifth straight year of double-digit growth—higher than India’s national average.
Which automotive sub-sectors will hire the most talent?
EV manufacturing, battery gigafactories, software-defined vehicle programs, ADAS development, charging infrastructure, and connected vehicle solutions will be the largest job creators.
What roles will emerge as new critical jobs in the automotive industry?
New-age job roles include battery recycling engineers, high-voltage safety specialists, cyber-resilience architects, autonomous navigation engineers, and digital twin simulation specialists.
Want deeper insights into automobile hiring trends, AI-based workforce transformation, and India’s talent demand outlook?
Download the full India Decoding Jobs 2026 report- complete data, hiring charts, industry forecasts & strategic recommendations.
Download Now- India Decoding Jobs 2026. Explore Taggd for RPO solutions.