Global Capability Centers (GCCs) in India have undergone a remarkable transformation. What began as cost-efficient offshore delivery centers have evolved into strategic innovation hubs driving enterprise-wide digital transformation.
Today, India accounts for over 50% of all GCC activity globally, with the market reaching $64.6B in FY2024 and projected to grow to $99–105B by 2030.
But here’s the challenge: success in this new era isn’t about building bigger teams, it’s about building scalable talent engines. These are sophisticated systems that can rapidly attract, develop, and deploy high-quality talent at speed, adapting to changing business needs while maintaining excellence.
As GCCs take on more strategic roles, from AI/ML leadership to R&D innovation, their ability to scale talent becomes the ultimate competitive advantage.
Why Talent Engines Matter More Than Ever?
The traditional GCC playbook of volume hiring is dead. Today’s leading GCCs are focused on talent velocity, the speed at which they can identify, onboard, and deploy skilled professionals across complex, high-value functions.
The new reality:
- 67% of new GCCs in India now lead mandates in AI/ML, automation, and engineering R&D
- 55% manage core finance functions including digital finance and risk operations
- Nearly half of GCC leaders plan to increase hiring in FY2026, but with a focus on fewer, more strategic roles
This shift from volume to value demands a fundamentally different approach, one that prioritizes agility, skills over titles, and continuous capability building.
Core Strategies GCCs Are Using to Build Scalable Talent Engines
Global Capability Centres (GCCs) in India are moving beyond traditional hiring models to create scalable talent engines that can meet rapid business demands and evolving skill needs.
They are adopting a mix of strategies- skill-first hiring, continuous upskilling through internal academies, and multi-tier city expansion to tap diverse talent pools. AI-driven recruitment and workforce planning are helping accelerate hiring while university and EdTech partnerships strengthen early-career pipelines.
Flexible work models, strong employer branding, leadership development, data-led talent management, and inclusion initiatives, including reverse brain drain programs, are further enabling GCCs to attract, develop, and retain high-quality talent at scale.
Let’s explore the strategies GCCs are using to build scalable talent engines in India:
1. Skills-First, Role-Second Hiring Strategy
Instead of focusing solely on degrees or years of experience, GCCs in India are prioritizing capability over credentials. This approach widens the talent pool by evaluating candidates on technical skills, problem-solving ability, and cultural fit.
By leveraging AI-driven candidate assessments and project-based evaluations, GCCs are ensuring they hire talent that can contribute from day one. Leading GCCs are also abandoning rigid job descriptions in favor of dynamic skills mapping.
These are the high-demand skills driving growth and shaping the future of GCC operations:
- Generative AI and Machine Learning (32% annual growth)
- Platform Engineering and DevOps
- Cybersecurity and Risk Management
- Data Science and Analytics
To effectively embed these capabilities into the workforce, GCCs are implementing:
- AI-powered skills assessments during screening
- Cross-functional skill matrices for internal mobility
- Continuous skills gap analysis and forecasting
2. Multi-Location Talent Hub Strategy
Tier-1 hubs such as Bengaluru, Mumbai, and Hyderabad remain the epicenters for complex R&D, innovation projects, and leadership functions. These cities offer a deep concentration of specialized talent, established technology ecosystems, and direct access to global clients, making them ideal for housing roles that demand niche technical expertise and high-touch client interaction.
Tier-1 Centers (Bengaluru, Mumbai, Hyderabad):
- Complex R&D and innovation roles
- Leadership and client-facing positions
- Specialized technical expertise
However, as per the GCC Report 2025, 40% of GCCs are diversifying beyond Tier-1 cities to achieving 50-60% cost savings while maintaining quality.
This will help GCCs build scalable talent engines and tap into untapped and cost-effective talent markets. Further, this reduces hiring competition in overcrowded metros while supporting regional economic growth.
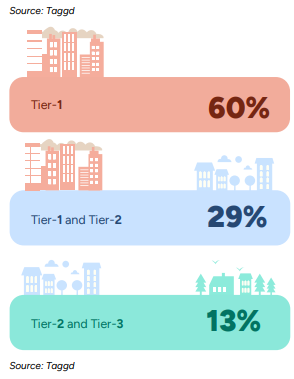
It also enables GCCs to offer hybrid and satellite office models, which appeal to professionals seeking better work-life balance.
Tier-2/3 Expansion (Jaipur, Kochi, Indore):
- Scalable operations and analytics
- Early-career talent development
- Cost-optimized delivery functions
3. Internal Talent Academies and Upskilling Ecosystems
To keep pace with fast-changing technologies, GCCs are investing in internal learning academies and tailored training modules. Forward-thinking GCCs are building comprehensive learning infrastructures that continuously evolve their workforce capabilities via upskilling programs.
These programs focus on niche skills such as cloud computing, cybersecurity, data analytics, and domain-specific expertise.
By creating a culture of continuous learning, GCCs not only retain talent but also reduce dependency on external hiring for critical roles
Core components:
- Just-in-time learning: Microlearning modules aligned to project needs
- Certification partnerships: With AWS, Microsoft, Google for cloud and AI skills
- Leadership development: Cross-cultural management and global client engagement
- Internal mobility programs: 60% of GCCs now have formal IJP frameworks
4. AI-Driven Workforce Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence is helping GCCs shortlist candidates faster, match roles to skills, and forecast workforce planning with remarkable accuracy. Automated resume screening, predictive analytics for attrition, and skill-gap analysis make hiring more efficient and scalable.
This data-driven approach ensures the right talent is in place for both current and future business needs.
Current adoption trends:
- 58% of GCCs are exploring AI tools in hiring
- Only 17% report satisfaction with current implementations
- Focus shifting from filtering to comprehensive talent intelligence
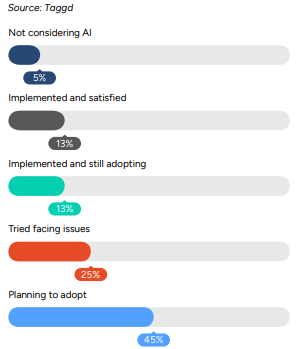
Applications:
- Attrition prediction and retention interventions
- Skills gap forecasting and proactive training
- Performance-based team composition
- Automated candidate experience management
5. Strategic Academia Partnerships
Many GCCs are building strategic alliances with universities and EdTech platforms to access fresh talent and co-create specialized courses. These collaborations help in shaping industry-ready graduates while securing a consistent inflow of trained entry-level professionals.
Partnership models:
- Joint curriculum development with IITs and IIITs
- Industry-sponsored research projects
- Paid internship programs with clear conversion paths
- Faculty exchange and knowledge sharing initiatives
Key Enablers of Scalable GCC Growth in India
India’s GCC expansion story is being powered by a strong foundation of supportive policies, cutting-edge infrastructure, and a highly evolved talent ecosystem. Together, these elements are enabling companies to scale operations rapidly while maintaining quality and innovation.
Government Policy Support
Government initiatives continue to be a strategic growth catalyst for GCCs. State-specific incentives such as Karnataka’s KATALYST program and Tamil Nadu’s GCC-focused policies are creating regionally competitive ecosystems.
At the national level, alignment with the Skill India Mission and FutureSkills Prime ensures that talent development is future-ready.
Additionally, the National Apprenticeship Programs offer structured entry pathways for young professionals, helping companies onboard and train talent at scale with minimal ramp-up time.
- State-specific incentives: Karnataka’s KATALYST, Tamil Nadu’s GCC policies
- Skill India Mission and FutureSkills Prime alignment
- National Apprenticeship Programs providing structured entry pathways
These policy interventions wouldn’t have their full impact without the physical and digital spaces that enable innovation to flourish.
Infrastructure Readiness
India’s commercial real estate sector is rising to meet GCC demands, with a record-breaking 28 million sq. ft. of office space leased by GCCs in 2024. The focus is on Grade A commercial spaces built to foster innovation, collaboration, and productivity.
Moreover, hybrid-first infrastructure ensures distributed teams can work seamlessly, integrating remote talent without compromising efficiency.
- Record-breaking 28 million sq ft office leasing by GCCs in 2024
- Grade A commercial spaces designed for innovation and collaboration
- Hybrid-first infrastructure supporting distributed teams
Yet, even the best policies and infrastructure depend on one factor above all, a skilled and adaptable workforce.
Talent Market Maturity
India’s talent market has evolved into a mature, globally competitive resource base. Deep STEM talent pools are spread across multiple cities, providing GCCs with flexibility in site selection.
The trend of reverse brain drain is bringing back experienced Indian professionals from global markets, infusing local teams with international expertise.
Furthermore, specialization in emerging technology domains, from AI to cybersecurity is expanding the country’s value proposition beyond cost efficiency to innovation leadership.
- Deep STEM talent pools across multiple cities
- Increasing reverse brain drain as global Indian talent returns
- Growing specialization in emerging technology domains
Navigating the Challenges for GCC Expansion in India
As India’s GCC sector scales, the road ahead is not without hurdles. Retention, skill availability, and competitive market dynamics are emerging as critical challenges that demand strategic responses.
The Retention Reality
- Average tenure varies significantly: 2.5-4.5 years depending on function
- Offer-to-join ratios: Range from 55% (AI/ML roles) to 70% (traditional functions)
- 39% of all GCC hires are replacement hires, highlighting retention challenges
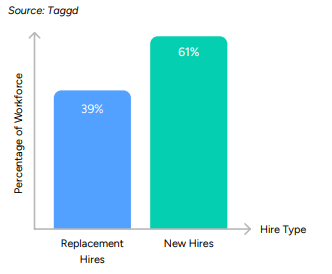
Beyond retaining talent, GCCs must also solve for skill gaps that hinder scaling.
Skills vs. Scale Dilemma
While India offers abundant talent, the challenge lies in finding the right skills at the right experience level:
- 50% of new hires expected to have less than 5 years of experience
- Limited availability of mid-senior level professionals in emerging tech
- Need for continuous reskilling as technology evolves
Adding to the complexity is a fiercely competitive market where the fight for talent is as much about brand perception as it is about pay.
Competition and Market Dynamics
The GCC ecosystem is experiencing intense competition for specialized talent, particularly in next-gen technology roles. Market cannibalization is becoming evident, as newer entrants lure candidates with premium compensation packages.
In this environment, a differentiated employer value proposition is no longer optional, it’s essential for attracting and retaining the right people.
- Intense competition among GCCs for specialized talent
- Market cannibalization as newer GCCs offer premium packages
- Need for differentiated employer value propositions
The Road to 2030: Future-Proofing Talent Strategies
GCCs can future-proof growth by decentralizing talent hubs, integrating AI-driven hiring intelligence, and fostering continuous reskilling programs, ensuring smarter, faster, and more adaptive workforce models to meet evolving global demands by 2030.
Emerging Trends Reshaping GCC Talent
Emerging GCC talent trends include India-based leadership gaining strategic control, expansion into Tier-2/3 cities with robust infrastructure, DEI moving from metrics to structural inclusion, Gen Z prioritizing growth and purpose, and AI evolving from basic screening to comprehensive talent intelligence for smarter workforce decisions.
- Power Shift: Strategic control gradually moving to India-based leadership
- Beyond Metro Comfort: Sustainable expansion into Tier-2/3 cities with proper infrastructure
- Purpose-Driven DEI: Evolution from performative metrics to structural inclusion
- Gen Z Career Expectations: Emphasis on growth, flexibility, and meaningful work
- AI as Framework: Moving beyond filtering to comprehensive talent intelligence
Strategic Imperatives for 2025-26
This section outlines the priority actions GCCs must take to sustain competitive advantage. These include adopting hybrid workforce models, leveraging outsourcing synergies, integrating start-up innovation, and embracing GCC-as-a-Service to accelerate market entry and scale efficiently.
- Distributed workforce strategies combining conventional and managed spaces
- Synergistic partnerships with outsourcing providers for specialized capabilities
- Start-up ecosystem integration for innovation and agile talent acquisition
- GCC-as-a-Service models for rapid market entry and scaling
Building Your Scalable Talent Engine: A Strategic Framework
This framework guides GCCs through three phases, laying the foundation with skills mapping and brand positioning, building systems via AI-driven hiring and upskilling, and finally scaling with multi-location hubs, predictive analytics, and continuous capability innovation.
Phase 1: Foundation Setting (Months 1-6)
- Skills mapping and gap analysis
- Location strategy and infrastructure planning
- Employer brand development and market positioning
- Initial talent pipeline creation
Phase 2: System Building (Months 6-18)
- Recruitment process optimization with AI integration
- Internal mobility and upskilling program launch
- Performance management and retention strategy implementation
- Partnership ecosystem development (academia, vendors, government)
Phase 3: Scale and Optimize (Months 18+)
- Multi-location talent hub operationalization
- Advanced workforce analytics and predictive planning
- Leadership development and succession planning
- Continuous innovation and capability enhancement
Wrapping Up: India’s Position as the Global Talent Capital
The data is clear: India isn’t just hosting GCCs, it’s defining the future of global capability development. With over 2.8-4 million GCC jobs projected by 2030, the opportunity is unprecedented.
However, success will belong to organizations that think beyond traditional hiring. The future lies in building talent engines that can learn, adapt, and scale, systems that combine human potential with technological capability to create sustained competitive advantage.
For GCC leaders, the question isn’t whether to invest in scalable talent strategies, it’s how quickly you can build the infrastructure to support tomorrow’s workforce, today.
Explore the complete strategies and insights for GCCs to build scalable talent engines in India. Download the complete GCC Report 2025: “Cracking the Growth Code for GCCs in India 2025”, a comprehensive report by Taggd, CII, and JLL India covering 100+ GCC leaders across the ecosystem.









