India’s manufacturing sector is on the brink of a transformative decade. Today it contributes 17% to the national GDP, but with capacity expansion, supply-chain diversification and policy reinforcement, India is targeting a steep rise to 25% by 2030. The sector, currently valued at $1.74 trillion, is expected to scale to $2.30 trillion by 2030, positioning India among the world’s leading industrial economies.
Adding momentum to this growth, the government plans to deploy $2.2 billion in incentives to strengthen domestic production, support global value chain integration, and accelerate Make in India. Manufacturing exports are also projected to touch $1 trillion by 2028, creating a much larger demand for skilled talent across factories, engineering clusters and advanced materials units.

Workforce expansion will follow. According to projections featured in Taggd’s India Decoding Jobs 2026 Report, the sector already employs 27.3 million people, and Foreign Direct Investment which has surged 69% in the past decade, with $383.5 billion flowing in over the last five years is set to unlock large-scale job creation in electronics, semiconductors, auto components, textiles, and green manufacturing.
Notably:
- 500,000+ new Industry 4.0 jobs could emerge as automation, IoT-enabled plants and smart factories move mainstream
- India needs 78.5 lakh non-farm jobs annually until 2030, and manufacturing will carry a major share of this demand
Together, these forces signal one unmistakable shift and 2026–2030 will be the most talent-intensive era of Indian manufacturing.
Get the full projection report in India Decoding Jobs 2026 — Download the report for CHRO-grade insights.
6 Major Hiring Trends Shaping the Manufacturing Industry in 2026
The Indian manufacturing industry is entering a high-growth hiring era, fueled by Industry 4.0 adoption, semiconductor investments, MSME-driven expansion, and increasing automation maturity.
With the sector projected to contribute 25% to India’s GDP by 2030, generate 1 million+ semiconductor jobs, and push exports toward a $1 trillion milestone, the demand for future-ready talent is set to surge across shopfloor, engineering, digital, and R&D functions.
2026 manufacturing hiring trends will be defined by hybrid skill sets, AI-augmented work, and a rapid shift toward connected, smart factories- making manufacturing one of India’s most aggressive talent-creation engines in the next five years.
Rapid Industry 4.0 Adoption
Smart factories are moving from concept to execution. Companies are scaling IoT-integrated production lines, machine-vision quality cells, automated material movement, and predictive maintenance systems.
What’s changing:
- ERP → MES → AI-linked factory systems
- Real-time sensor monitoring & cloud dashboards
- Fully digitised production and downtime analytics
Hiring demand will surge for:
- IoT Engineers & Automation Software Specialists
- Digital Twin Developers & Real-time Data Analysts
- Predictive Maintenance Engineers & SCADA/MES Integrators
Rise of Additive Manufacturing & 3D Printing
3D printing is now moving beyond prototyping and tooling into high-volume commercial production, especially in aerospace, auto components, medical devices and custom industrial parts.
What’s changing:
- Faster product development cycles
- Customisation at scale
- Reduced scrap and material waste
Job roles gaining momentum:
- Additive Manufacturing Technicians
- Design Optimisation & CAD/CAE Engineers
- Nanomaterials and Powder Metallurgy Experts
Semiconductor Expansion = Massive Job Creation
With India’s semiconductor mission accelerating, chip fabs, ATMP units, display fabs, and OSAT facilities are expected to create 1 million+ jobs by 2026.
What’s driving hiring:
- Multi-billion-dollar fab investments
- Local sourcing & packaging ecosystem growth
- Talent demand across R&D to clean-room operations
Skills in demand:
- Wafer Fabrication Engineers
- Photolithography & Deposition Specialists
- Yield Improvement & Failure Analysis Engineers
- Clean-room Operation & Supply Chain Experts
Human-Machine Collaborative Roles
Rather than replacing people, automation is unlocking new hybrid work models where humans supervise, program, and guide machines.
What’s shifting:
- Operators → Automation Partners
- Technicians → Robotics Supervisors
- Shop Floor Roles → Human-AI Co-execution
Hiring will favour:
- Robotics & Cobots Operators
- AI-enabled Production Planners
- Automation Troubleshooting Technicians
Upskilling becomes mission-critical- digital, programming & robot-handling skills will define employability going forward.
The Era of Hybrid Talent: Mechanical + Digital + AI
Manufacturing talent is no longer conventional. The most valuable professionals will blend mechanical understanding with AI fluency, PLC logic and data analytics.
New skill DNA emerging:
- Mechanical engineering + Python
- Robotics + IoT + PLC programming
- Lean + Digital quality control systems
High-growth job categories:
- PLC/SCADA Engineers with Data Interpretation Skills
- AI-Aware Production Managers
- Robotics-Aligned Machine Operators
- Cybersecurity for Industrial Systems
MSME-Led Growth Will Drive Regional Hiring Waves
With 43% of PLI white-goods applicants being MSMEs, smaller manufacturers are becoming large-scale job creators- particularly across auto ancillaries, textiles, electronics, consumer durables, and precision manufacturing clusters.
What to expect
- State and district-level hiring spikes
- Higher demand for general technicians, QC, supervisors
- Increased apprenticeships & skill-based vocational hiring
Skills and roles that will rise:
- CNC/Lathe Operators, QA Inspectors, Tool Room Techs
- Line Supervisors, Maintenance Electricians
- Production Foremen & Lean Manufacturing Technicians
Regional Manufacturing Hubs & Future Hiring Heat-Zones
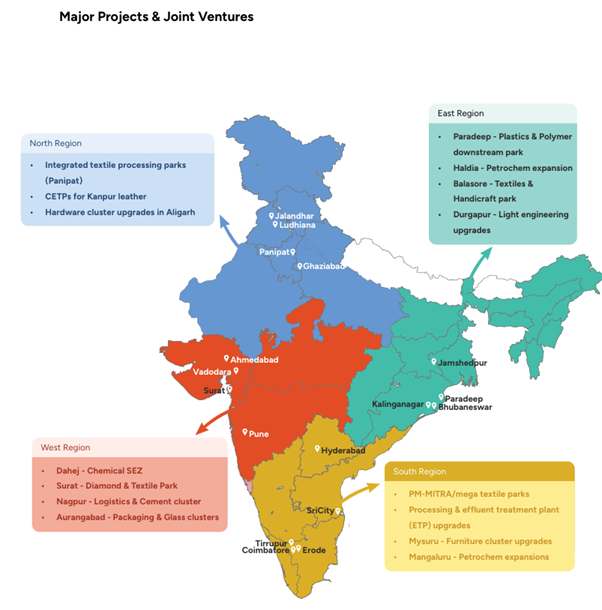
India’s manufacturing landscape is becoming spatially diverse, with growth no longer concentrated in traditional belts alone. New clusters are emerging across the North, West, South, and East- driven by sector-specific strengths such as textiles, petrochemicals, electronics, steel, and automotive engineering.
These hubs are supported by industrial corridors, PLI schemes, freight connectivity, and a rapidly scaling skilled workforce, making them central to India’s march toward a $1 trillion manufacturing export economy.
Check out the Key Industry Players Driving India’s Manufacturing Ecosystem:
| Region | Key Cities / Nodes | Public & Private Companies | Major Projects & Joint Ventures | Main Focus Areas |
| North | Ludhiana, Jalandhar, Panipat, Kanpur, Aligarh, Ghaziabad | Vardhman Textiles, Trident, Nahar Group, JK Cement, Leather MSMEs (Kanpur), Aligarh lock cluster | – Integrated textile processing parks (Panipat) – CETPs for Kanpur leather – Hardware cluster upgrades in Aligarh | Textiles, leather goods, paper, sports goods, hardware |
| South | Coimbatore, Tiruppur, Erode, Karur, Tuticorin | Shahi/Kitex (textiles) TNPL (paper) MRPL-linked clusters Garment MSMEs | – PM-MITRA/mega textile parks – Processing & effluent treatment plant (ETP) upgrades – Mysuru furniture cluster upgrades – Mangaluru petrochem expansions | Textiles & garments, home textiles, paper & packaging, petrochemicals, furniture |
| West | Ahmedabad, Surat, Vadodara, Nagpur, Nashik, Raigad, Aurangabad | Ambuja, Grasim, UltraTech, L&T (Heavy Engg.), Reliance (Chemicals), Garment & textile clusters in Surat | – Dahej chemical SEZ, Surat Diamond & Textile Park – Nagpur logistics + cement cluster – Aurangabad packaging & glass clusters | Textiles (Surat), cement, chemicals & polymers, heavy engineering, glass & packaging |
| East | Kalinganagar, Paradeep, Jamshedpur, Bhubaneswar, Haldia, Durgapur | Tata Steel Downstream Products, Vedanta (aluminium products), Haldia Petrochemicals, Paradeep Plastics Park, Handloom MSMEs in Odisha & Bengal | – Paradeep plastics & polymer downstream park – Haldia petrochem expansion – Balasore textiles & handicraft park – Durgapur light engineering upgrades | Petrochemicals, plastics, aluminium downstream, textiles & handicrafts, light engineering |
Key Challenges in Manufacturing Hiring
The manufacturing ecosystem is entering a period of accelerated evolution. Automation, digital transformation, and new energy transitions are reshaping everything from plant design to workforce structures.
While the opportunities are massive, the challenges in talent acquisition are equally critical, especially as factories modernise, product cycles compress, and competition for multi-skilled labour intensifies.
Without the right talent strategy, organisations risk rising production delays, cost overruns, and an inability to scale during peak growth windows.
Below are the most pressing barriers affecting manufacturing hiring today as per the findings from India Decoding Jobs Report 2026.
1. Skills & Digital Talent Gap
The global manufacturing workforce is expected to fall short by 7.9 million people by 2030, resulting in potential revenue losses of $607 billion. This isn’t just a vacancy problem- it’s a capability gap.
Where the shortage is most visible:
- Industrial automation & robotics
- PLC/SCADA system handling
- Mechatronics & AI-assisted production
- Cybersecurity for OT/IT systems
- Predictive maintenance & digital twin ops
Factories are digitising faster than people are upskilling- widening the demand-supply divide every year.
2. High Attrition Across Shop Floor Roles
Attrition currently ranges between 40–45% in several manufacturing clusters.
This leads to:
- Frequent retraining costs
- Production loss due to onboarding lag
- Reduced shift continuity & process stability
- Increased pressure on supervisors & team leads
Retention is now as important as recruitment.
3. Automation-Driven Role Shifts
With generative AI and automation projected to impact up to 30% of work hours by 2030, job contours are transforming rapidly.
Hiring isn’t just about manpower- it’s about future-proof skill composition, including:
- Robotics handling
- Machine-learning-assisted quality checks
- Sensor analytics & energy efficiency monitoring
- Human–machine collaborative workflow capability
Talent needs to be digital-ready on Day Zero.
4. Regulatory, Trade & Compliance Complexity
76% of manufacturers cite geopolitical uncertainty as a major operational risk due to tariffs, export restrictions, environmental compliance shifts, and evolving labour laws.
For HR teams, this translates into:
- Hiring delays due to documentation requirements
- Difficulty sourcing compliant workforce pipelines
- Rising demand for EHS, ESG & compliance professionals
- Increased risk of audit penalties when hiring is rushed
A recruitment function built for agility is no longer optional.
How Taggd Helps Manufacturers Solve These Hiring Challenges
Taggd bridges the gap between manufacturing industry demand and workforce availability through domain-specialised RPO models tailored for manufacturing.
| Hiring Challenge | Taggd Advantage | Outcome for Enterprises |
| Skills shortage in next-gen roles | Pan-India access to skilled workforce across automation, PLC, AI-ops, maintenance | Faster hiring for high-tech & blended manufacturing roles |
| 40–45% attrition pressure | Predictive hiring backed by data intelligence, culture fit screening | Lower churn, stable shifts, higher productivity |
| Automation-led role transitions | Skill adjacency mapping + upskilling collaborations with training partners | Future-ready talent without long learning curves |
| Regulatory & compliance complexity | 100% audit-driven hiring, statutory compliance, process transparency | Zero non-compliance hiring risk, smoother global audits |
What Taggd Delivers for Manufacturing Hiring
- AI-enabled talent discovery from India’s largest digital recruitment network
- Industry-specific talent intelligence & salary benchmarking
- Shop-floor, technician, and specialised engineering hiring at scale
- Capability to supply workforce across Automotive, Electronics, Metals, Textiles, Chemicals, and more
- Data-backed hiring predictability that reduces time-to-fill and cost-per-hire
- Access to a pre-assessed talent pool for faster deployment
Result: Better talent. Lower attrition. Faster plant readiness.
Manufacturers who plan workforce transformation now will lead the next decade — and Taggd is built to help them get there.
Future Hiring Trends for FY26–27 in India’s Manufacturing Sector
India’s manufacturing sector is set to witness one of its strongest growth cycles between FY26 and FY30, fuelled by large-scale investments in semiconductors, electric vehicles, renewable energy, advanced electronics and smart factory infrastructure.
With PLI incentives accelerating domestic production, the hiring landscape will shift dramatically, especially for digital-first, automation-ready roles.
As the industry moves from labour-intensive processes to high-tech, digitally integrated manufacturing, demand will rise sharply for hybrid talent equipped with robotics, automation, IIoT, data analytics, additive manufacturing and semiconductor engineering skills.
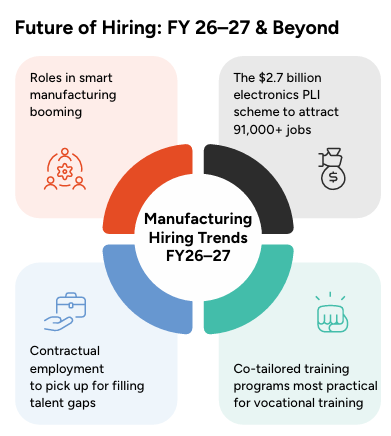
Smart Factory Talent Surge (2026–27 Outlook)
Smart manufacturing adoption is accelerating, and so is skills demand.
- IIoT, predictive maintenance and robotics roles will grow exponentially
- IIoT-led maintenance can reduce machine downtime by up to 22%
- Smart shop floors can cut maintenance costs by nearly 30%
- 36% of employers already report rising demand for tech-integrated roles in manufacturing
This shift will create premium job opportunities for professionals who can blend operational understanding with digital tools, data systems and automation controls.
Electronics PLI to Unlock New Job Creation
The $2.7 billion Electronics PLI scheme, expected to attract nearly $7 billion in investment and create ~91,000 new jobs, will boost hiring for:
- PCB engineers & technicians
- Semiconductor process specialists
- Display & component assembly operators
- Electronics testing, QA & failure analysis engineers
With the semiconductor ecosystem scaling, talent will become the new competitive differentiator.
Hiring Models Will Evolve Fast
The skills gap is widening. Many MSMEs report that existing training programmes are insufficient- 71% of small manufacturers say current skilling support falls short. As a result, hiring strategies will diversify:
| Rising Approach | Why it Matters |
| Contract & temporary workforce | Helps fill short-term gaps quickly amid talent shortages |
| Apprenticeships & ITI partnerships | Builds steady pipelines of shop-floor ready technicians |
| Co-developed training programs | Reduces dependency on external skilling schemes |
| In-house upskilling for hybrid roles | Future-proofs the workforce against automation shifts |
Companies that invest early in workforce capability will scale faster and at lower cost than competitors who delay talent transformation.
Wrapping Up
India’s manufacturing sector is entering a defining decade- one shaped by Industry 4.0, smart factory adoption, semiconductor growth, and an expanding domestic production ecosystem.
As automation accelerates and investments scale, the competition for skilled talent will intensify across technical, engineering, and hybrid manufacturing roles. Employers who invest in workforce development today will lead tomorrow’s industrial transformation.
From high technology fabs to sustainable materials and precision engineering, the next wave of growth will demand speed, skill, and strategic hiring execution.
This is where a specialised recruitment partner like Taggd becomes critical in helping businesses build future-ready teams, reduce hiring time, bridge skill shortages, and scale workforce capability seamlessly.
The future of manufacturing is not just industrial- it is digital, intelligent, and talent-powered. Those who build the right talent foundations now will define India’s manufacturing story for the next 25 years.
To get deeper insights into Manufacturing hiring trends, AI-based workforce transformation, and India’s talent demand outlook, download the full India Decoding Jobs 2026 report- complete data, hiring charts, industry forecasts & strategic recommendations.
Download Now- India Decoding Jobs 2026.






