Master Work Behavior Tips for a Thriving Workplace
The Shifting Landscape of Work Behavior in India
The Indian workplace is transforming dramatically. Evolving employee expectations are reshaping the definition of “good” work behavior, compelling organizations to rethink their engagement and performance management strategies. Traditional approaches to motivating and retaining employees are losing effectiveness, and new challenges demand fresh solutions.
Declining Engagement and Shifting Priorities
One of the most significant shifts has been a decline in employee engagement. This is especially pronounced in India, where engagement levels have dropped sharply. In 2025, Indian employee engagement fell to 19%, down from 24% in 2024, the steepest global decline according to ADP Research’s ‘People at Work 2025’ study. This contrasts with the global rise in engagement. While 33% of Indian workers feel part of a top team, second-highest globally, overall engagement remains low. This underscores the urgent need for organizations to understand and address the causes of disengagement.
Understanding the Dynamics of Work Behavior
Understanding the types of work behavior is crucial to address these challenges. The infographic below visualizes their distribution:
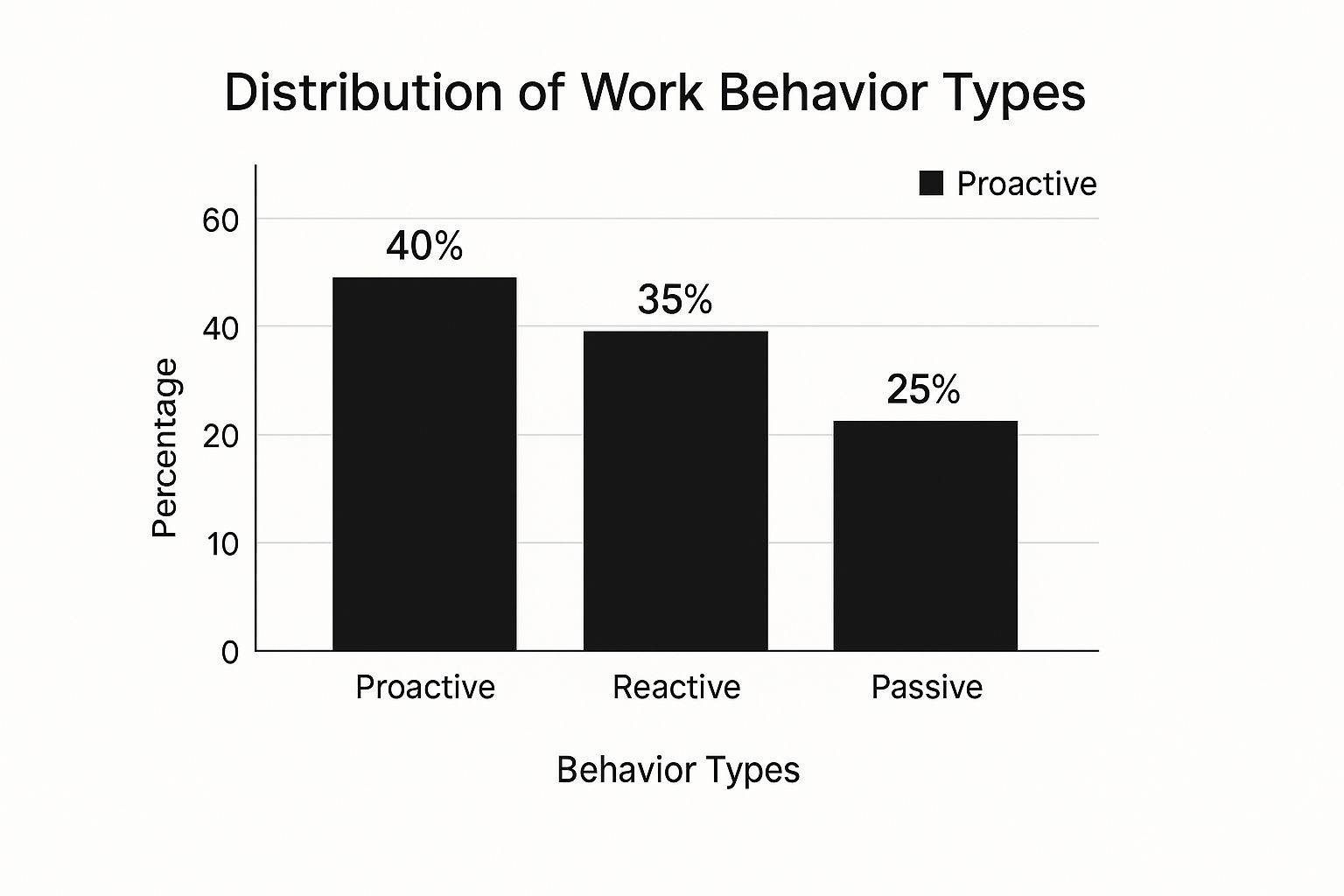
Proactive behavior, marked by initiative, comprises 40% of observed behaviors. Reactive behavior, responding to situations as they arise, accounts for 35%. Passive behavior, with a lack of initiative, represents 25%. Organizations need to foster a culture that encourages proactivity and minimizes passive and reactive behaviors. This means empowering employees to take initiative and contribute meaningfully.
The following table presents a closer look at employee engagement metrics in India, comparing key indicators and their impact on work behavior.
Employee Engagement Metrics in India A comparison of key engagement indicators and their impact on work behavior
| Engagement Metric | Current Level (%) | Year-over-Year Change (%) | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overall Engagement | 19 | -5 | Reduced productivity and innovation |
| Feeling Part of a Top Team | 33 | N/A | Potential for increased collaboration, but impacted by low overall engagement |
| Proactive Behavior | 40 | N/A | Drives innovation and positive change |
| Reactive Behavior | 35 | N/A | Can hinder efficiency and strategic planning |
| Passive Behavior | 25 | N/A | Negatively impacts productivity and morale |
This data highlights the interconnectedness of engagement metrics. While a significant portion of employees feel part of a strong team, the overall low engagement and prevalence of passive behavior suggest underlying issues impacting the entire workforce.
The Impact on Organizational Performance
Changing work behavior significantly impacts organizational performance. Declining engagement and rising passive behavior can reduce productivity, innovation, and growth. However, by understanding these evolving dynamics, organizations can proactively create a more engaged workforce. Strategies might include flexible work arrangements, improved communication, and a focus on employee well-being. These efforts are crucial for navigating the challenges and leveraging the opportunities presented by India’s shifting work landscape.
How Gen Z Is Redefining Work Behavior Norms
A noticeable shift is happening in India’s workplaces as Gen Z begins their careers. This generation brings fresh perspectives and work behaviors, actively reshaping workplace norms. Their influence is evident in evolving collaboration models, communication styles, and career paths, presenting both opportunities and adjustments for organizations across India.
The Rise of Gen Z in the Indian Workplace
Gen Z is rapidly becoming a significant presence in the Indian workforce. Projections indicate they will represent approximately 27% of the total workforce by 2025. This influx of younger workers, with their distinct expectations and work styles, will significantly impact company cultures and workplace priorities.
This means over a quarter of Indian employees will prioritize flexibility, mental health resources, and meaningful work experiences. Learn more about Gen Z in the Indian workforce. Companies must adapt their operations and management strategies to accommodate these shifting priorities.
Redefining Collaboration and Communication
Gen Z’s approach to collaboration often differs from previous generations. Growing up with digital tools like Slack has shaped their preference for instant communication and remote teamwork. This familiarity has fostered a preference for flatter organizational structures and collaborative projects.
Gen Z also values open and direct communication, prioritizing feedback and transparency. This shift requires leaders to adopt more inclusive and collaborative management styles. Regular feedback sessions and open-door policies are becoming increasingly important for effective team management. This new style also emphasizes emotional intelligence and active listening in workplace interactions.
Shifting Career Trajectories
Gen Z is also transforming career paths in India. Unlike earlier generations who often prioritized job security and linear career progression, Gen Z emphasizes work-life balance and personal growth.
They’re more inclined to change jobs to find roles aligned with their values and offering skill development opportunities. This trend requires companies to adapt their talent management strategies. Providing growth and development opportunities is key to retaining these employees. Organizations also need to cultivate a supportive environment that respects work-life balance and acknowledges individual contributions.
Bridging the Generational Gap
This evolving work behavior landscape also presents the challenge of bridging the generational gap. Friction can arise between Gen Z’s preferences and the established norms of older generations. Companies must create inclusive environments accommodating diverse work styles.
Strategies like intergenerational mentoring programs and workshops focusing on communication styles can help bridge this divide. What Millennials and Gen Z Expect from Employers in India offers further insights. Successfully navigating these evolving work behaviors will be vital for organizations in India to flourish in the coming years.
Breaking the Cycle of Toxic Work Behavior

Toxic work behavior poses a serious threat to organizations throughout India. These behaviors, ranging from subtle microaggressions to blatant bullying, can significantly impact productivity, stifle innovation, and contribute to high employee turnover. Effectively addressing this challenge requires a deep understanding of its root causes and the implementation of practical strategies for intervention and prevention.
Identifying Toxic Work Behaviors
Toxic behavior in the workplace manifests in various ways. Recognizing these behaviors is the first step towards creating a healthier work environment. Some common examples include:
- Bullying: This involves repeated aggressive actions directed at an individual or group, fostering a hostile atmosphere.
- Harassment: Unwanted conduct based on protected characteristics, leading to an intimidating, offensive, or humiliating experience.
- Discrimination: Unfair or prejudicial treatment based on factors such as caste, religion, gender, or age.
- Microaggressions: Subtle, often unintentional, everyday expressions of bias or prejudice that can accumulate and create a hostile environment.
- Gossiping and Rumor Spreading: These actions can erode trust and cultivate a culture of suspicion within the workplace.
- Passive-Aggression: Indirect resistance to requests or demands, often expressed through behaviors like procrastination or negativity.
Left unchecked, these behaviors cultivate a psychologically unsafe environment, hindering individual performance and negatively impacting overall well-being.
The Real Cost of Toxicity
The repercussions of toxic work behavior are extensive. For individuals, it can manifest as stress, anxiety, diminished job satisfaction, and even physical health problems. From an organizational perspective, the costs include reduced productivity, lower morale, increased absenteeism, and difficulties in retaining valuable talent.
Workplace toxicity continues to be a significant challenge in India. The 2024 Gallup State of the Global Workplace Survey indicates that 86% of Indian employees reported experiencing struggles in their work environment. Furthermore, the issue of underreporting remains prevalent, highlighting the fear of repercussions faced by many employees. A study of nearly 1,200 companies revealed that 788 reported zero complaints in 2023-24, despite rising complaint averages across organizations. Find more detailed statistics here.
Breaking the Cycle: Intervention and Prevention
A multi-pronged approach is crucial for effectively addressing toxic work behavior. Key elements of this approach include:
- Clear Policies: Implementing comprehensive policies that clearly define acceptable workplace behavior and establish procedures for reporting violations.
- Training and Education: Providing training to all employees, including managers, on identifying and addressing toxic behaviors.
- Open Communication: Fostering a culture of open communication where employees feel safe reporting issues without fear of retaliation.
- Prompt Investigation: Taking all complaints seriously and ensuring thorough and impartial investigations.
- Accountability: Holding individuals accountable for their actions and implementing appropriate disciplinary measures. Explore our guide on managing employees.
- Building Psychological Safety: Creating a psychologically safe environment where employees feel respected, valued, and empowered to speak up.
This involves setting clear expectations, modeling respectful behavior from leadership down, and actively promoting open dialogue.
Creating a Culture of Respect
Ultimately, breaking the cycle of toxic work behavior hinges on establishing a culture of respect. This extends beyond simply addressing individual incidents; it requires cultivating an environment where positive work behavior is actively valued and reinforced.
Key strategies include:
- Recognizing and Rewarding Positive Behavior: Celebrating and acknowledging employees who consistently demonstrate positive work behaviors.
- Promoting Teamwork and Collaboration: Encouraging collaboration and providing opportunities for employees to build positive relationships.
- Providing Support and Resources: Offering resources such as employee assistance programs and counseling services to support employees navigating challenging situations.
Consider exploring Talent Hired for assistance in building a more positive workplace environment. By proactively addressing toxic behavior and investing in a healthy workplace culture, organizations in India can unlock their full potential and create a truly thriving environment for all.
Leveraging Flexibility To Transform Work Behavior
The relationship between flexibility and positive work behavior is more complex than many leaders realize. While offering flexibility can boost engagement and productivity, it can also decrease accountability and create communication issues if not implemented thoughtfully. This section explores how Indian organizations are leveraging flexible work models to reshape employee behavior and the keys to their success.
Flexibility: A Double-Edged Sword
The ongoing debate surrounding remote versus in-office work often overlooks a critical point: flexibility alone does not guarantee improved work behavior. In fact, poorly planned flexible work arrangements can negatively impact work behavior. For example, a lack of clear communication protocols in a hybrid model can easily lead to misunderstandings and frustration, ultimately harming team cohesion. Conversely, well-structured flexible models can improve both autonomy and accountability, resulting in a more engaged and productive team.
Flexibility Models and Their Impact on Work Behavior
Different flexibility models yield different outcomes. To illustrate this, let’s consider the following comparison:
To help understand the varying effects of flexible work models, the table below provides a comparison across several key performance indicators.
| Flexibility Model | Engagement Impact | Productivity Impact | Retention Impact | Implementation Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fully Remote | Can increase if managed effectively, decrease with potential isolation | Potential increase with eliminated commute, potential decrease with home distractions | Can improve, particularly for certain demographics | Requires robust communication and performance management |
| Hybrid | Can promote work-life balance, but requires clear guidelines | Potential for improved focus, dependent on task and individual | Can attract talent prioritizing flexibility | Requires careful scheduling and allocation of resources |
| Flexible Hours | Can increase employee autonomy and motivation | Can optimize individual peak productivity periods | Can improve work-life integration and retention | Requires clear communication regarding employee availability |
| Compressed Workweek | Can enhance focus due to fewer workdays | Potentially increased daily output due to longer workdays | May improve employee morale and reduce burnout | May not be suitable for all roles or industries |
This table highlights how each model presents unique advantages and disadvantages, especially concerning employee engagement and productivity. Selecting the right model depends on various factors, including team dynamics, the nature of the work tasks, and the overall organizational culture.
Key Factors for Success
Several key factors influence whether flexible work arrangements positively impact behavior:
- Leadership Practices: Leaders who demonstrate trust and clearly communicate expectations create an environment where employees can thrive in flexible settings.
- Communication Systems: Establishing effective communication channels is vital for seamless collaboration in any flexible work environment. Utilizing platforms like Slack can facilitate efficient communication.
- Performance Metrics: Focusing on outcomes, rather than physical presence, is crucial for successful flexible work arrangements. This results-oriented approach motivates employees to deliver results, regardless of location or schedule. Implementing a performance management system can assist in tracking and measuring these outcomes.
Building a Culture of Flexibility and Accountability
Successfully implementing flexible work requires cultivating a culture that values both flexibility and accountability. This involves the following:
- Establishing Clear Expectations: Defining performance standards and communication protocols upfront helps to eliminate ambiguity.
- Providing Resources and Training: Providing employees with the tools and training necessary for effective remote work boosts productivity. This can involve providing access to collaboration tools and project management software, training on best practices, and ensuring adequate technical support.
- Fostering Trust and Autonomy: Empowering employees to manage their own time and workload builds trust and strengthens their sense of responsibility. This might involve offering flexible work schedules or remote work options.
- Maintaining Team Cohesion: Regular virtual team meetings, social events, and informal communication channels help maintain strong team connections and prevent feelings of isolation among remote team members. This also includes opportunities to enhance communication and interpersonal skills within the team.
By carefully considering these factors, organizations in India can harness flexibility as a valuable tool to transform work behavior, creating a more engaged, productive, and ultimately successful workforce.
Building Trust: The Foundation of Positive Work Behavior

Trust is fundamental to positive work behavior. It’s not just a nice-to-have; it’s the foundation upon which productive teams and successful organizations are built. This section explores the vital role of trust in shaping work behavior, particularly within Indian organizations. We’ll discuss how a lack of trust can lead to counterproductive actions and examine practical strategies for cultivating and rebuilding trust within teams.
The Consequences of Low Trust
A lack of trust can significantly impact work behavior. When employees don’t trust their leaders or colleagues, they may withhold information, worried that sharing it could be detrimental. Defensive communication can also become commonplace, breeding suspicion and hindering open collaboration. This means vital information might not be shared, feedback could be misinterpreted, and opportunities for innovation might be missed.
Low trust often breeds risk aversion. Employees hesitant to take risks may avoid proposing new ideas or challenging existing processes. This can stifle innovation and limit an organization’s adaptability to evolving market conditions. Essentially, low trust hinders progress, impacting both individual and organizational growth.
Recognizing the Signs of Trust Erosion
Identifying early signs of trust erosion is crucial for intervention before it significantly affects work behavior. Several indicators can suggest declining trust within a team:
- Decreased Communication: A noticeable reduction in open communication, especially regarding sensitive topics, can be a warning sign.
- Increased Conflict: Frequent conflicts and misunderstandings may signal underlying trust issues.
- Reduced Collaboration: A reluctance to collaborate on projects or share information suggests a lack of trust between team members.
- Declining Morale: Low morale, disengagement, and increased cynicism can indicate a trust deficit.
These consistent indicators warrant attention and proactive intervention from leadership.
Cultivating Trust: Practical Strategies
Building and restoring trust requires conscious effort and consistent leadership. Here are a few effective strategies:
- Lead by Example: Leaders must embody trustworthiness through transparent communication, impartial decision-making, and by keeping commitments. This sets the standard for the entire organization and cultivates a culture of integrity.
- Create Psychological Safety: Employees need to feel comfortable expressing opinions, sharing concerns, and taking calculated risks without fear of negative consequences. This encourages open communication and collaboration.
- Facilitate Open Communication: Establish consistent channels for feedback, both formal and informal, to address concerns and build understanding. This could involve one-on-one discussions and team meetings for open dialogue.
- Repair Damaged Relationships: When trust has been broken, directly addressing the root causes and working towards reconciliation is essential. This might involve mediation, guided conversations, or team-building exercises.
Building Trust in Indian Organizations
Many successful Indian organizations actively assess trust levels and implement trust-building programs. They utilize surveys, feedback sessions, and focus groups to understand employee perceptions of trust. This data informs targeted interventions to address specific trust gaps within teams and departments. These organizations understand that trust isn’t just a “soft” skill; it’s a vital driver of performance and a key component of a positive and productive work environment. By prioritizing trust, these organizations establish a solid foundation for positive work behavior and sustainable growth.
Actionable Strategies to Transform Work Behavior
This section offers practical strategies to reshape work behaviors within your organization, focusing on frameworks relevant to the Indian workplace. We’ll explore successful behavior transformation initiatives and discuss how to motivate desired behaviors, address problematic ones, and embed behavioral expectations within your company culture.
Designing Effective Recognition Programs
Recognition programs can significantly reinforce positive work behavior. However, strategic design is crucial to avoid creating dependency. Instead of relying solely on monetary rewards, consider incorporating a mix of approaches:
- Public Acknowledgement: Recognizing achievements during team meetings or company-wide announcements can be highly motivating.
- Opportunities for Growth: Offering training, mentorship, or leadership roles as rewards fosters professional development.
- Peer-to-Peer Recognition: Implementing systems for colleagues to acknowledge each other’s contributions strengthens team bonds and reinforces positive behaviors.
These strategies promote intrinsic motivation and cultivate a culture of appreciation.
Implementing Collaborative Performance Systems
Performance systems should encourage collaboration and avoid unhealthy competition. Consider these approaches:
- Team-Based Goals: Setting shared objectives fosters collaboration and a sense of collective responsibility, creating a supportive environment.
- Skill-Based Assessments: Evaluating employees based on their skills and contributions, rather than solely on individual output, recognizes the value of diverse skill sets and helps identify areas for development.
- 360-Degree Feedback: Gathering input from multiple sources, including peers, supervisors, and subordinates, offers a holistic view of performance and encourages constructive feedback, promoting transparency and continuous improvement.
These collaborative systems drive team synergy and individual growth.
Developing Effective Mentorship Initiatives
Mentorship programs transmit positive work behaviors by providing role models and guidance. Here’s how to maximize their effectiveness:
- Structured Programs: Formal mentoring programs with clear objectives, matching criteria, and regular check-ins ensure focus and support, increasing the likelihood of achieving desired outcomes.
- Training for Mentors: Equipping mentors with skills in communication, feedback, and identifying developmental opportunities helps them guide their mentees effectively.
- Mentoring Across Departments: Encouraging cross-departmental mentoring exposes mentees to diverse work styles and perspectives, fostering broader organizational understanding and breaking down silos.
These initiatives can significantly influence work behavior across the organization. For further reading on related topics, see A Guide to Ease Online Recruitment Process for HR Professionals.
Equipping Middle Managers
Middle managers are key to implementing these strategies and addressing problematic behaviors. Provide them with:
- Training on Conflict Resolution: Equip managers with the skills to mediate conflicts, address difficult conversations, and promote respectful communication, potentially through role-playing, case studies, and practical exercises.
- Clear Communication Protocols: Establish clear procedures for handling behavioral issues, ensuring consistency and fairness, reducing ambiguity, and promoting accountability.
- Resources and Support: Provide access to resources such as HR support, employee assistance programs, and legal counsel to help managers address sensitive situations appropriately, demonstrating organizational commitment.
By implementing these practical, actionable strategies, organizations can cultivate a positive and productive work environment. Consider partnering with Taggd to implement talent management solutions and improve work behavior across your organization.
