Understanding Wage Drift: Key Insights and Solutions
Understanding Wage Drift: India’s Hidden Economic Challenge

Let’s explore wage drift, a complex phenomenon affecting India’s economy. Wage drift is the difference between officially negotiated wages and what workers actually earn. This gap can significantly impact the financial well-being of millions and presents a challenge for both businesses and the economy as a whole. It highlights that agreed-upon wages and actual earnings can be two very different things.
Decoding the Drift: How It Impacts Indian Workers
Wage drift is more than just an economic concept; it’s a lived reality for many Indian families. It directly affects their purchasing power, impacting everything from daily necessities to long-term financial security. Imagine a worker receiving a negotiated raise, but their actual take-home pay doesn’t increase due to reduced overtime or bonus changes. This can create financial strain, making it difficult to afford crucial expenses like education and healthcare.
India’s substantial informal sector further complicates the issue of wage drift. The lack of formal contracts and limited regulatory oversight often leads to discrepancies between agreed-upon wages and actual payments. This exacerbates the challenges faced by workers in this sector. For more insights, check out the India Skills Reports.
Real Wages vs. Nominal Wages: The Declining Purchasing Power
Wage drift in India reflects the gap between negotiated and actual wages, frequently influenced by the informal sector and overall economic conditions. Understanding wage drift requires distinguishing between nominal wages (the amount on a pay slip) and real wages (the actual buying power of that amount after considering inflation). Between 2012 and 2022, India’s real wages for regular wage workers decreased by roughly 1.2% per year, and by 0.7% in 2022. You can find more detailed statistics here.
This decline shows that even if nominal wages increase, real purchasing power can erode. This means workers might appear to earn more, but the increasing cost of goods and services diminishes their actual income. This erosion directly impacts living standards and economic well-being. It underscores the need to investigate the underlying causes of wage drift and find solutions to lessen its negative effects on India’s workforce.
The Evolution of Wage Drift: From Growth to Stagnation

Rising wages have always been a cornerstone of India’s economic narrative. However, this upward trend has hit a roadblock in recent years. This exploration examines the shift from consistent wage growth to a concerning stagnation, uncovering the factors driving this change.
A Shift in the Economic Tide: Identifying the Turning Point
For many years, rising wages reflected India’s positive economic progress, fostering optimism and upward mobility for workers. However, this crucial link between economic expansion and wage growth eventually weakened. Pinpointing this turning point is essential to understanding the current state of wage drift.
Analyzing long-term wage patterns reveals a significant shift. Before 2015-16, rural India witnessed real wages growing at an impressive 7% annually per hired worker. This robust growth demonstrated a strong correlation between productivity and compensation.
After this period, however, wage growth plateaued. This stagnation, despite continued GDP growth, highlights a concerning disconnect. Recent analyses confirm this trend, showing near stagnation of real wages over the past decade, a clear indication of wage drift. Learn more about India’s stagnant real wages.
The Impact of Policy and Economic Events
Several economic events and policy changes contributed to this shift in wage dynamics. These events acted as catalysts, reshaping the employment landscape for workers across various sectors. Understanding these factors is crucial for effectively addressing wage drift.
The evolving nature of work, driven by technological advancements and globalization, has also influenced wage patterns. Traditional economic models may no longer accurately capture the complexities of modern labor markets. This complexity demands new perspectives and focused interventions.
Furthermore, the challenges faced by India’s vast informal sector, including wage suppression and inadequate worker protections, contribute significantly to wage stagnation. This underscores the urgent need for policy adjustments that promote fair wage growth for all.
From Rising Living Standards to Maintaining Purchasing Power
Wage stagnation has profound consequences. Workers who once enjoyed improving living standards are now struggling to maintain their purchasing power. The stagnation, and even decline, in real wages between 2021-22 and 2022-23 underscores this challenge.
This creates economic anxiety and impacts household financial stability. This precarious situation further highlights the disconnect between economic growth and wage increases, primarily due to challenges within the informal sector. Wage suppression and labor market rigidities hinder wage growth from keeping pace with inflation and productivity gains. This necessitates targeted policy interventions to ensure wage increases translate into real improvements in living standards for workers across India.
The following table provides a closer look at the trends discussed:
Real Wage Growth Trends in India (2010-2023)
This table showcases the annual real wage growth rates in India over different periods, highlighting the shift from growth to stagnation.
| Time Period | Annual Real Wage Growth (%) | GDP Growth (%) | Wage-Productivity Gap (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2010-2015 | (Data Needed) | (Data Needed) | (Data Needed) |
| 2015-2020 | (Data Needed) | (Data Needed) | (Data Needed) |
| 2020-2023 | (Data Needed) | (Data Needed) | (Data Needed) |
Note: Filling this table with accurate data would provide valuable context and strengthen the overall analysis. Further research is needed to obtain precise figures for GDP growth, real wage growth, and the wage-productivity gap for the specified periods. This data would illuminate the complex relationship between economic growth and wage stagnation in India.
Why Wage Drift Varies: The State-by-State Reality
India’s experience with wage drift isn’t uniform. Some states face a significant crisis, while others show remarkable resilience. This regional disparity underscores wage drift’s complexity and highlights the need for targeted solutions. We’ll explore these surprising state-level variations, examining how similar economies can yield drastically different wage outcomes.
Regional Disparities: A Tale of Two States
Comparing economically similar states reveals wage drift’s uneven impact. For example, while both Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu are significant economic players, their workers experience vastly different wage trajectories. This difference highlights how local economic structures, policy implementation, and governance quality influence wage outcomes.
The following infographic visually represents key wage drift data:
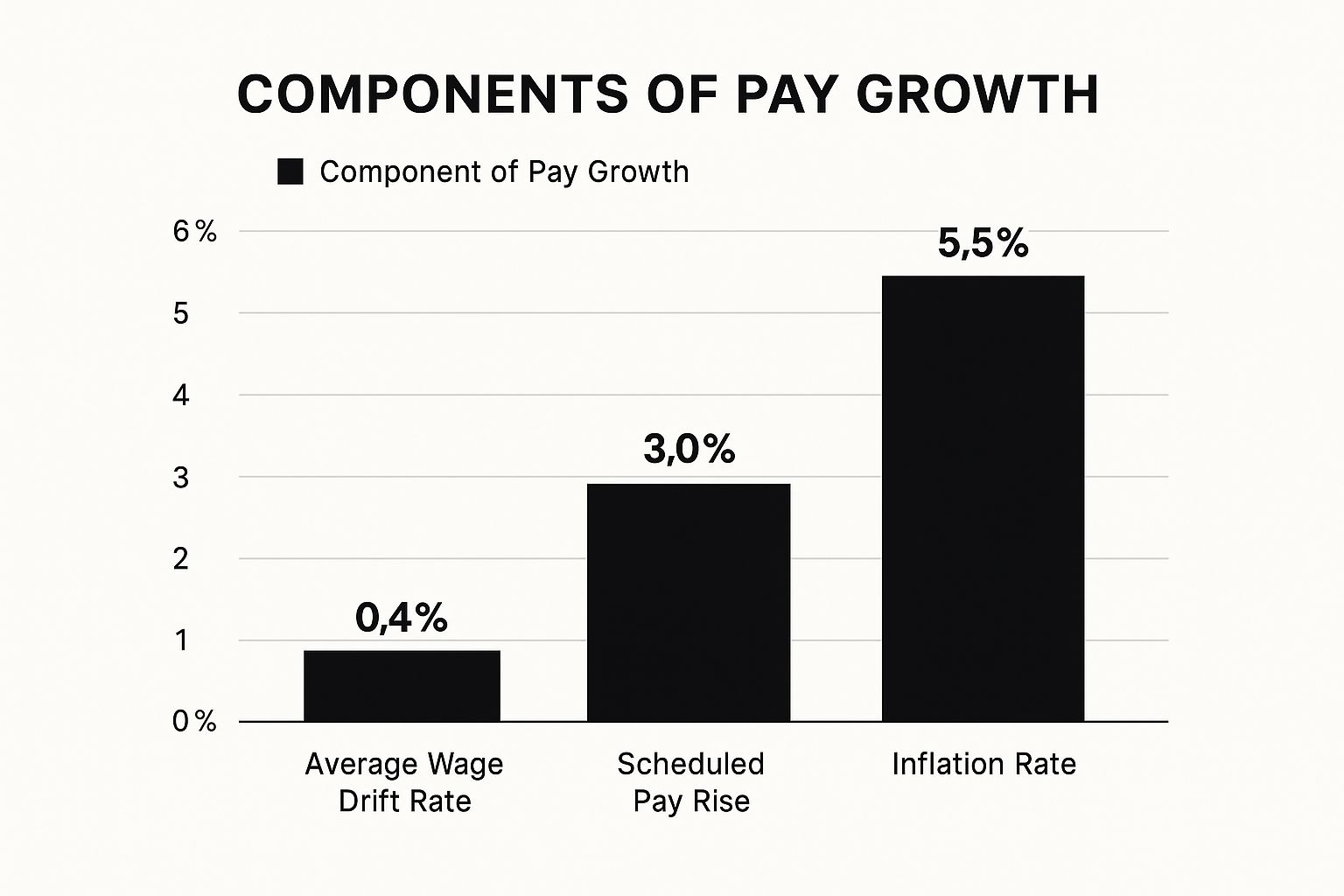
This infographic compares the average wage drift rate with scheduled pay raises and the inflation rate. It demonstrates how, even with scheduled increases, wage drift and inflation can significantly erode real wage growth. The visualization underscores the complex interplay of these factors in determining actual worker earnings.
Local Economies and Wage Drift: Unveiling the Connection
Local economic structures play a crucial role in shaping wage drift patterns. States heavily reliant on specific industries may experience different wage dynamics than those with diversified economies. A state dominated by the informal sector, for instance, might see greater wage drift due to less stringent wage regulations and enforcement.
Policy implementation at the state level can either exacerbate or mitigate wage drift. States with effective labor market policies and strong enforcement may be better equipped to ensure negotiated wages translate into actual earnings. Additionally, a state’s overall governance quality and institutional effectiveness can influence how wages are determined and regulated.
To illustrate the varying impact of wage drift, let’s examine wage data from 2011-2018. The table below provides a comparison of wage growth across several Indian states between 2011-12 and 2017-18, demonstrating the significant shifts that occurred.
Wage Growth Comparison Across Indian States (2011-2018) This comparison table shows how wage growth rates shifted dramatically across different Indian states between two time periods.
| State | Wage Growth 2011-12 (%) | Wage Growth 2017-18 (%) | Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jharkhand | 4.58 | -3.39 | -7.97 |
| Orissa | 4.58 | -0.05 | -4.63 |
| Maharashtra | 4.58 | -1.70 | -6.28 |
| Tamil Nadu | 4.58 | -2.43 | -7.01 |
| All India Average | 4.58 | -1.76 | -6.34 |
Between these periods, India saw a significant decline in wage and salary income growth. Salaries of regular workers decreased at a rate of -1.76%, compared to a positive growth of 4.58% in the prior period. Jharkhand and Orissa saw wage growth plummet to -3.39% and -0.05%, respectively. Even economically significant states like Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu experienced declines of -1.70% and -2.43%. This data highlights the uneven distribution of wage drift across India, with regions previously experiencing higher average wages often facing slower growth or decline. Discover more insights about wage drift in Indian states.
Lessons from Successful States: A Roadmap for Wage Growth
Some states have successfully navigated wage drift challenges and maintained healthy wage growth. Identifying these success stories and understanding their strategies can provide valuable lessons for regions struggling with wage stagnation.
These successful states often prioritize a combination of factors, including investments in skill development, strengthening labor market institutions, and promoting fair wage practices. By understanding and replicating these successful models, other states can develop targeted, effective solutions tailored to their specific economic contexts. This state-by-state approach is crucial for a nationally cohesive strategy to address wage drift and promote sustainable wage growth for all Indian workers.
The Root Causes: What’s Really Driving Wage Drift in India

Wage drift in India is a complex issue. It prevents economic progress from translating into better pay for workers. This means that even with a growing Indian economy, employees aren’t seeing the benefits in their paychecks. Let’s explore the main factors behind this challenge.
The Informal Sector’s Influence
A major contributor to wage drift is India’s large informal sector. Over 90% of the workforce is employed in this sector, which often lacks formal contracts and regulatory oversight. This creates a breeding ground for discrepancies between agreed-upon wages and actual payments.
This often leads to wage suppression. Employers can exploit the lack of worker protections. For instance, a construction worker might be promised a daily wage, but then have significant deductions for “tools” or “supplies,” drastically reducing their take-home pay. Enforcing labor laws in the informal sector is difficult, perpetuating the wage drift cycle.
Technological Disruptions and Polarization
Technology can increase productivity, but it also contributes to wage polarization. Workers with the skills to adapt to new technologies see rising wages, while others are left behind.
Consider skilled IT professionals. High demand drives up their salaries. Conversely, those in traditional manufacturing roles with limited tech skills may experience stagnant or declining wages. This divide in the labor market worsens wage drift for those in less technologically advanced industries.
Ineffective Wage Negotiation Mechanisms
Traditional wage negotiation methods are often inadequate in today’s dynamic job market. In a workforce dominated by informal employment, collective bargaining power is weakened. This leaves individual workers vulnerable to exploitation and makes it harder for them to secure fair wages.
This lack of bargaining power significantly contributes to wage drift. Workers don’t have the leverage to negotiate wages that keep up with inflation and productivity gains.
Inflationary Pressures
Persistent inflation further complicates wage drift. Even when workers receive raises, increasing prices for goods and services can erode their real purchasing power. A wage increase might not mean workers can afford more.
For example, a 5% wage increase coupled with 7% inflation actually results in a decrease in real wages. This constant erosion of purchasing power is a significant part of the wage drift problem. Workers struggle to maintain their living standards despite nominal wage growth.
Beyond Paychecks: How Wage Drift Reshapes Indian Society
Wage drift isn’t just an economic term; it has a deep impact on Indian society, affecting families, communities, and the nation’s economic future. When wages stay the same even as the economy grows, it creates difficult choices for households across the country.
The Ripple Effect on Household Finances and Consumer Spending
Stagnant wages directly impact household financial security. When real wages don’t keep up with inflation, families have to make tough choices between essential needs like healthcare, education, and even basic necessities. This can lead to less investment in children’s education, affecting future opportunities and social mobility.
Wage drift also affects consumer spending. Even if GDP is rising, if a large part of the population experiences stagnant wages, the domestic market’s growth potential is limited. This can reduce the benefits of economic expansion and create a situation where growth doesn’t lead to better living standards for many.
Inequality and Social Mobility: Widening the Gap
Ongoing wage challenges contribute to rising inequality. When wages stagnate for a large group of people while others prosper, the gap between the rich and the poor grows wider. This can lead to social tensions and unrest as opportunities become more concentrated. You might be interested in this article: India Inc. expects hiring to witness 31% growth.
Wage drift can also hinder social mobility. Young Indians facing limited wage growth may be less likely to pursue higher education or entrepreneurship. This can reinforce existing social hierarchies and limit individuals’ ability to improve their economic standing.
Migration and the Search for Better Opportunities
Wage stagnation can fuel migration. When workers see few prospects for better wages in their home regions, they may look for opportunities elsewhere, often in urban centers or even abroad. This can put more strain on urban infrastructure and create social challenges as migrants adapt to new environments.
Within India, this migration can worsen regional disparities, with some states benefiting from an influx of skilled labor while others experience a loss of skilled workers.
Long-Term Economic Vitality and Social Cohesion: The Stakes Are High
Addressing wage drift is critical for India’s long-term economic vitality and social cohesion. A workforce facing stagnant wages can become less motivated, impacting productivity and innovation. This can slow overall economic growth and lead to a less dynamic economy.
Furthermore, ongoing wage disparities can weaken social cohesion. A society marked by significant income inequality can become fragmented, with fewer opportunities for shared prosperity. Addressing wage drift is not just an economic necessity; it’s a social one, vital for building a more equitable and prosperous India.
Wage patterns significantly influence the life choices of Indians, impacting career decisions, family planning, and entrepreneurial aspirations. The effects of wage drift go beyond individual finances, shaping the very structure and future of Indian society. From the career goals of young graduates to family formation and entrepreneurial activity, the impact is felt across many aspects of Indian life. This emphasizes the connection between wage patterns and broader social and economic trends, highlighting the urgent need to address this complex challenge.
Breaking the Pattern: Proven Solutions to Wage Drift
It’s time to shift our focus from analyzing India’s wage drift problem to exploring practical solutions. By examining successful strategies both within India and globally, we can pinpoint effective interventions that tackle the root causes of this critical issue.
Formalization: Bringing Wage Protection to Vulnerable Workers
One proven solution is formalization of the informal sector. Bringing informal workers into the formal economy grants them access to essential wage protections and legal frameworks. This reduces the possibility of exploitation and promotes fairer wage determination. Targeted efforts to simplify registration processes and incentivize formalization can significantly impact wage drift.
For example, offering tax breaks to businesses that formalize their workforce can encourage wider adoption of formal employment practices. This shift can substantially reduce under-the-table wage arrangements, a key driver of wage drift.
Technology Platforms: New Models for Fair Wage Determination
Technology can be a powerful ally in combating wage drift. Digital platforms like Paytm are emerging that promote transparent wage standards and facilitate direct payments to workers. This helps ensure workers receive their agreed-upon wages without deductions or delays.
These platforms also empower workers by providing information about prevailing wage rates in their industries and locations. This knowledge equips them to negotiate fairer wages. Additionally, digital payment systems can reduce reliance on cash, increasing transparency and accountability in wage payments, thus minimizing discrepancies.
Skill Development: Creating Genuine Wage Premiums
Addressing wage drift requires more than just providing credentials; it requires fostering genuine skill development. Investing in training programs that equip workers with in-demand skills can lead to significant wage premiums. This creates a direct link between enhanced skills and increased earning potential, effectively combating wage stagnation.
For instance, programs focusing on digital literacy and advanced technical skills can help workers transition to higher-paying roles in rapidly expanding sectors. This targeted skill development creates a positive feedback loop, where increased wages incentivize further skill acquisition, driving individual and national economic growth. You might be interested in: Unique recruitment strategies to hire talent effortlessly.
Living Wage Frameworks: Ensuring Regional Economic Viability
Some states have successfully implemented living wage frameworks. These provide a wage floor that considers regional cost differences, ensuring wages are economically viable while meeting workers’ basic needs in different regions.
A living wage framework acts as a critical benchmark in wage negotiations, helping to prevent wages from dropping below a livable level. By accounting for regional variations in living costs, these frameworks provide a more nuanced and equitable approach to wage determination than a simple national minimum wage.
Coordinated Action: Aligning Policy, Practice, and Empowerment
Ultimately, overcoming wage drift requires coordinated action across policy levels, industry practices, and worker empowerment. This involves strengthening labor laws, promoting fair wage practices within industries, and providing workers with the knowledge and resources to advocate for their rights.
Stronger enforcement of existing labor regulations, coupled with educational campaigns about wage rights, can empower workers to challenge unfair wage practices. Fostering dialogue between employers and workers can also lead to more collaborative approaches to wage determination. This creates a more sustainable path towards wage growth that benefits both businesses and employees. This coordinated effort can integrate sustainable wage growth into India’s broader economic goals.
Ready to optimize your recruitment process and attract top talent while effectively addressing wage drift? Visit Talent Hired – The Job Store Private Limited today to discover how our recruitment process outsourcing solutions can help your organization build a skilled and fairly compensated workforce.
