Workforce Automation in India: Key Changes and Benefits
The Rise of Workforce Automation in India

India is quickly becoming a major player in workforce automation. Businesses across the country are changing how they operate, thanks to the growing use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and other automation technologies. This shift is impacting India’s economy, creating both opportunities and challenges. Automation’s influence extends beyond technology itself, affecting hiring practices and the skills needed for tomorrow’s jobs.
AI’s Growing Presence in India
India’s leading role in AI is clear. The country’s AI workforce has grown by a remarkable 33.4% year over year, showing a strong investment in this technology. This growth is especially noteworthy compared to global trends. Industries like IT, finance, and manufacturing are being transformed by this increase in AI adoption, leading to gains in efficiency and productivity. But this growth also raises questions about the future of work and the essential skills for success in an automated world. This rapid expansion of AI has a direct impact on workforce dynamics. For more information on this growth, check out this article: India Leads Global AI Workforce Growth at 33.4%
For instance, workforce engagement in India dropped to 19% in 2025, down from 24% in 2024. This suggests that while AI is creating jobs, it’s also disrupting existing roles and processes. This highlights the need for strategies to reskill and upskill the workforce. NASSCOM, a prominent Indian IT industry body, estimates that nearly 69% of jobs could be affected by automation in the next two decades. This prediction underscores the need for individuals and organizations to adapt to the changing job market.
Impact on Industries
The effects of workforce automation are not the same across every industry. Some sectors, such as manufacturing and logistics, are seeing faster changes than others. This is due to differences in how easily automation can be adopted and the specific needs of each industry. For example, using robotics in manufacturing has greatly improved production efficiency. But it has also raised concerns about job displacement for workers in these areas.
The service industry is also being transformed by the rise of AI-powered customer service tools. These tools automate routine tasks, freeing up human agents to handle more complex customer interactions. This emphasizes the growing importance of human skills, such as empathy and problem-solving, even as automation increases. The growing use of automation across different industries highlights the need for strategic workforce planning and development. Preparing the workforce for the evolving demands of the job market is crucial for India’s continued economic growth and competitiveness.
Which Industries Are Being Transformed First?
Workforce automation isn’t a monolithic force impacting all industries equally. Its effects vary across different sectors of the Indian economy. Some industries are experiencing rapid shifts due to their inherent compatibility with automation technologies, while others are adapting at a slower pace.
Automation’s Front-Runners
Here are some industries at the forefront of automation adoption:
- Manufacturing: This sector is undergoing substantial changes as robots take on tasks like assembly line operations, quality control, and even complex manufacturing processes. For instance, automotive plants are using robotics for welding and painting, leading to greater precision and speed while minimizing human error. Learn more about the Rising Potential for Jobs in Automotive Industry.
- Logistics: Warehousing and delivery are being revolutionized by automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and sophisticated routing systems. This optimization enhances efficiency and speeds up delivery times, significantly impacting e-commerce and supply chain management.
- Customer Service: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are handling routine customer inquiries, allowing human agents to focus on more complex issues. This improves efficiency and enables 24/7 customer support.
- IT: Automation is simplifying software development, testing, and deployment processes. This includes using AI for code generation, bug detection, and automated testing, freeing up IT professionals for more strategic tasks.
Impact on the Workforce
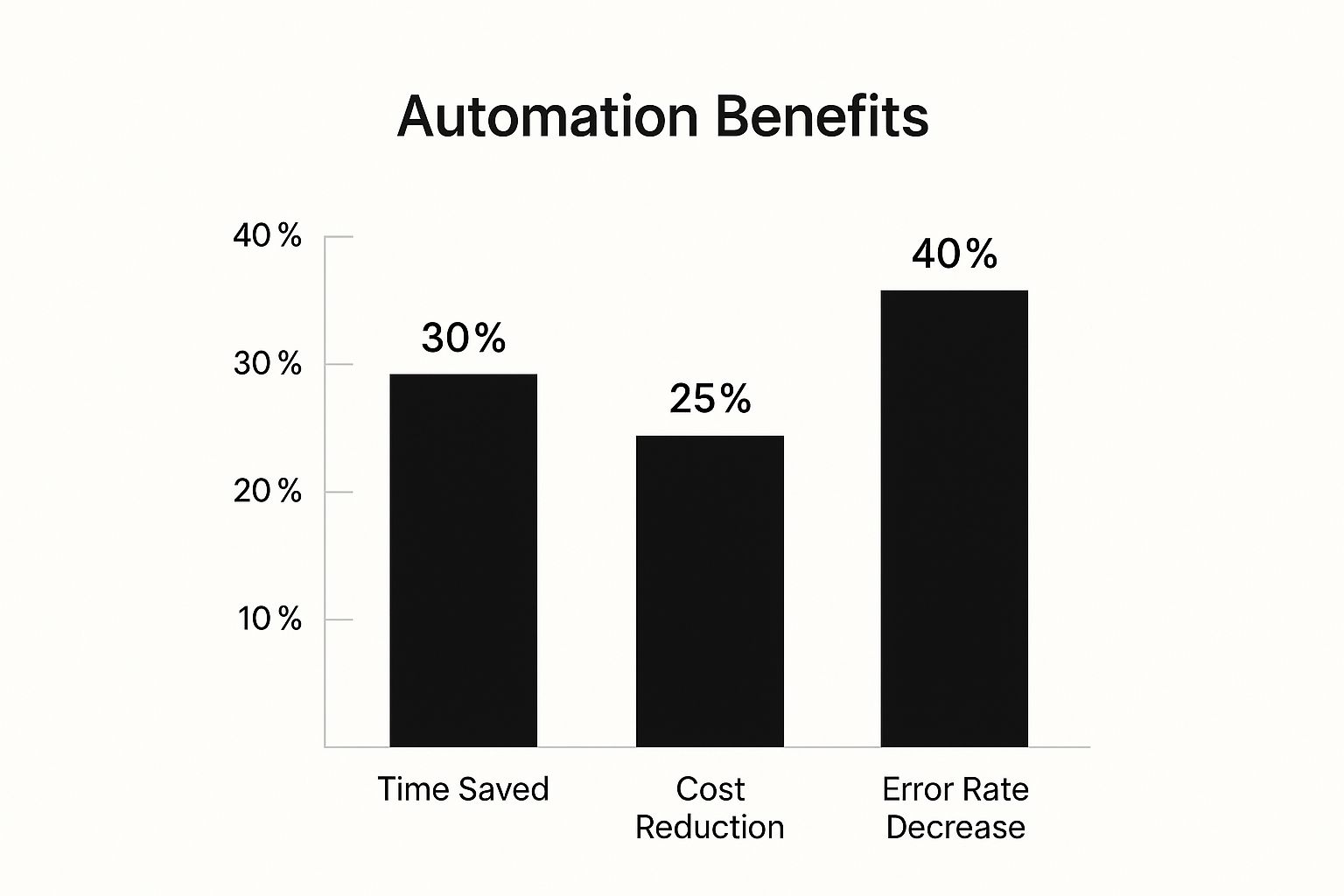
The infographic above illustrates key benefits of workforce automation, including a 30% increase in time saved, 25% cost reduction, and a significant 40% decrease in error rates. These figures highlight automation’s potential to improve organizational efficiency and performance.
However, these advancements come with challenges. India’s job market faces a significant skill gap. While demand for skilled professionals who can collaborate with AI and automation is growing, only 42.6% of Indian graduates are considered employable according to the Mercer-Mettl’s 2025 index. In sectors like manufacturing, up to 23% of existing roles could be automated, emphasizing the urgent need for upskilling and reskilling programs. Learn more about India’s job market and skill gap.
To illustrate the varied impact of automation across different sectors, let’s examine the following table:
Automation Impact Across Indian Industries
Comparison of automation adoption levels, job displacement risks, and new role creation across major sectors of the Indian economy
| Industry | Automation Level | Jobs at Risk (%) | New Roles Created | Required Skills |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | High | 23 | Robotics Technicians, Automation Engineers | Robotics, Programming, Maintenance |
| Logistics | Medium | 15 | Supply Chain Analysts, Data Scientists | Data Analysis, Logistics Management |
| Customer Service | Medium | 10 | AI Trainers, Conversational Designers | AI/ML, Communication, Customer Service |
| IT | High | 5 | Cloud Architects, Cybersecurity Specialists | Cloud Computing, Security, DevOps |
The table highlights that while manufacturing faces a higher risk of job displacement due to automation, it also creates new roles requiring specialized skills. Similarly, the growing adoption of automation in logistics and customer service is driving demand for professionals with expertise in data analysis and AI.
The Need for Adaptation
The shift towards automation underscores the importance of continuous learning and adaptation. Businesses must invest in training programs that equip their employees with the skills needed to succeed in this evolving environment. For individuals, proactively acquiring new technical skills and developing in-demand expertise is essential for navigating the changing job market.
This transformation isn’t simply about replacing jobs; it’s about redefining them. As automation handles routine tasks, new roles requiring human creativity, problem-solving, and critical thinking will emerge. The future of work in India demands a strategic and collaborative approach to workforce development, ensuring that businesses and individuals are prepared for the opportunities and challenges that automation presents.
The Double-Edged Sword: Job Losses Vs. New Opportunities

Workforce automation presents a complex scenario for India’s job market. It’s a story of disruption and creation, with some jobs disappearing as new ones emerge. Understanding this duality is crucial for individuals, businesses, and policymakers.
Navigating the Changing Job Landscape
Automation is reshaping industries across India, impacting various roles and demographics differently. Routine manual tasks are particularly susceptible, putting those jobs at risk.
However, this shift also fuels demand for professionals skilled in managing and maintaining automated systems. This necessitates workforce adaptation by acquiring relevant skills and expertise.
Some demographics are more vulnerable. Workers in sectors with high automation potential, like manufacturing and logistics, face greater displacement risks. Conversely, young professionals trained in emerging fields like AI and data science are poised to benefit from growing demand.
The Regional Impact of Automation
Automation’s impact varies regionally across India. Metropolitan areas and tech hubs typically see faster adoption, creating both opportunities and challenges. The availability of skilled professionals and infrastructure drives implementation across various industries in these areas.
However, rural communities may experience a slower pace with different implications for local economies. Bridging this regional divide through targeted policies and initiatives is vital for equitable distribution of automation’s benefits.
Automation: A Catalyst for Innovation
Automation isn’t just about job displacement; it fosters innovation and growth. The World Economic Forum projects that automation could create 97 million new roles globally by 2025. This is particularly relevant for India’s growing AI sector. While some jobs, especially in manufacturing and logistics, are at risk, new avenues open in AI development, data science, and digital transformation. Learn more about how automation is shaping India’s job market.
Strategies for Success in an Automated World
Individuals and organizations need proactive strategies to thrive in an automated workplace. For individuals, upskilling and reskilling are crucial. This involves proficiency in areas like data analysis, AI, and automation-related technologies. Cultivating soft skills like problem-solving, critical thinking, and adaptability is equally important.
Organizations must prioritize workforce development and a culture of continuous learning. Investing in training programs and supporting employees through the transition ensures they remain competitive and productive. Collaboration between industry, academia, and government is essential for developing effective training programs and policies that meet the evolving needs of the workforce.
This balanced perspective, addressing both job losses and new opportunities, is key to harnessing automation’s full potential in India. A proactive, strategic approach can ensure a more inclusive and prosperous future for its workforce.
Bridging the Skills Gap in an Automated Economy

India faces a significant challenge: a growing disparity between existing workforce skills and the evolving needs of businesses in an automated economy. This skills gap poses a major obstacle to India’s continued economic progress. Overcoming this requires a collaborative effort from employers, educators, and policymakers. For a more in-depth look at the current skills landscape, check out the India Skills Report 2023.
Identifying In-Demand Skills
The rise of automation has reshaped the skills needed to thrive. Technical skills, such as proficiency in AI, machine learning, and data analytics, are increasingly in demand. For instance, businesses need data scientists to analyze the large volumes of data produced by automated systems. Data analytics and Machine Learning are becoming very important for businesses to succeed. Robust cybersecurity measures are also vital for protecting sensitive data in our interconnected world.
Human skills, however, remain essential. These include critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication. As automation handles routine tasks, creativity and adaptability become highly valued. The ability to collaborate effectively and adapt to change is crucial in today’s dynamic work environment.
The table below provides a more detailed overview of the essential skills needed for success in India’s automated economy. It highlights current and projected demand, along with resources for skill development and relevant industry applications.
Critical Skills for India’s Automated Workforce Overview of the most valuable skills for workers in an automated economy, showing skill categories, demand levels, and development pathways
| Skill Category | Current Demand | Future Demand Projection | Development Resources | Industry Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Analytics | High | Very High | Online Courses, University Programs, Certifications | IT, Finance, Healthcare, Marketing |
| Machine Learning | Moderate | Very High | Online Courses, University Programs, Specialized Certifications | IT, Manufacturing, Research, Robotics |
| Cybersecurity | High | Very High | Certifications, Specialized Training Programs, Industry Workshops | IT, Finance, Government, Healthcare |
| Critical Thinking | High | High | Online Courses, Workshops, Mentorship Programs | All Industries |
| Communication | High | High | Workshops, Online Courses, Professional Development Programs | All Industries |
This table clearly demonstrates the growing importance of both technical and human skills. Investing in these areas will be key for individuals and organizations seeking to thrive in the automated economy.
Addressing the Education Gap
Traditional education systems often struggle to keep up with the rapid pace of technological advancements. This gap leaves many graduates ill-equipped for the demands of today’s workplaces. Recognizing this, many institutions are incorporating more practical, skills-based training into their curricula.
Progressive institutions are collaborating with industry partners to develop curricula that align with current and anticipated industry needs. This includes integrating emerging technologies into coursework and offering real-world experience through internships and apprenticeships. These partnerships help equip graduates with relevant skills and knowledge.
Innovative Approaches to Upskilling
Companies are also taking proactive steps to upskill their existing workforce. This includes providing internal training programs, supporting external certifications, and establishing mentorship programs. Some are even implementing “learning in the flow of work” initiatives. These allow employees to acquire new skills while working on projects, promoting continuous development.
Numerous success stories illustrate the positive impact of strategic upskilling. Workers who have embraced these opportunities have transitioned into new roles within their companies or even embarked on entirely new career paths. These stories highlight the transformative power of reskilling and upskilling initiatives.
Pathways to Automation-Resistant Capabilities
Building automation-resistant capabilities is vital for long-term career success. This requires individuals to be proactive in recognizing emerging skills gaps and pursuing relevant learning opportunities. Cultivating a growth mindset is essential for embracing lifelong learning and adapting to change. Continuously updating your skills will help you remain valuable in an ever-evolving job market.
Shaping the Future: Policy and Corporate Responses
Workforce automation presents significant challenges and opportunities for India. How are government and corporate leaders responding to these evolving circumstances? This complex issue requires a multifaceted approach involving policy adjustments, corporate initiatives, and public-private partnerships.
Government Initiatives and Policy Landscape
The Indian government recognizes the potential of workforce automation and is taking steps to address the accompanying challenges. Several initiatives focus on promoting digital literacy and skills development, including the National Digital Literacy Mission and the Skill India program. These programs aim to equip the workforce with relevant skills for an automated economy.
However, challenges remain. Policies concerning reskilling and upskilling need further development to effectively address potential job displacement caused by automation. More targeted programs focusing on specific industries undergoing rapid automation are crucial. Furthermore, improving access to these programs for vulnerable populations, particularly in rural areas, is essential. Learn more in our article about How Recruitment Process Outsourcing Can Help in High-Impact Hiring.
Corporate Responses and Best Practices
Forward-thinking companies in India are adopting worker-centric automation strategies. These organizations understand that balancing innovation with social responsibility is vital for long-term success. They are implementing reskilling programs to help employees transition into new roles within the company. Some are also investing in continuous learning initiatives to ensure their workforce remains adaptable in a changing environment.
For example, some companies offer employees paid time off for training and development, demonstrating a commitment to workforce upskilling. Others are providing mentorship programs connecting experienced employees with those transitioning into new roles. These practices cultivate a culture of continuous learning and support employees as they navigate changes.
Public-Private Partnerships and Emerging Models
Effective workforce development requires collaboration. Emerging public-private partnerships in India are creating innovative models to address the skills gap. These partnerships leverage the strengths of both sectors: corporations offer practical training and experience, while government agencies provide funding and policy support. This ensures training programs align with the needs of businesses.
One successful model involves establishing industry-specific training centers. These centers offer specialized training in high-demand areas like AI, robotics, and data science, equipping workers with practical skills. This collaborative approach bridges the gap between education and industry requirements.
Global Comparisons and Lessons Learned
Examining how other countries are handling workforce automation provides valuable insights for India. While each nation has unique circumstances, certain trends emerge. Countries successfully transitioning to an automated economy generally focus on early investment in education and skills development, coupled with strong social safety nets to support displaced workers.
By learning from other countries, India can develop more effective policies and strategies for managing the transition to an automated economy. This comparative approach helps ensure that the benefits of automation are widely distributed while mitigating negative employment impacts. This proactive approach is crucial for building a resilient and adaptable workforce capable of thriving in the age of automation.
Your Automation Survival Guide: Practical Next Steps
Workforce automation is changing India’s job market. This requires both individuals and organizations to adapt for continued success. This section offers practical strategies for navigating the future of work, whether you’re an employee or an employer.
Strategies for Individuals: Charting Your Course
Individuals can be proactive to stay competitive in an automated world. Here’s a roadmap:
- Embrace Lifelong Learning: Continuous learning is essential. Identify growing skills gaps and actively pursue opportunities to upskill. Online courses, certifications, and workshops can provide valuable knowledge in areas like data analytics, AI, and cybersecurity.
- Focus on Human-Centric Skills: While technical expertise is important, “soft skills” are also critical. Cultivate abilities like critical thinking, problem-solving, creativity, and communication. These are harder for automation to replicate.
- Network and Build Connections: Connect with industry professionals through online platforms like LinkedIn and in-person events. Networking offers valuable insights into industry trends, job opportunities, and emerging skill needs.
- Craft a Future-Proof Resume and Portfolio: Highlight your adaptable skills and showcase projects demonstrating your ability to work with automation. A strong portfolio showcases your practical experience and skills.
Strategies for Organizations: Leading the Transition
Organizations play a vital role in supporting their workforce during this transformation. Here’s how:
- Foster a Culture of Continuous Learning: Create opportunities for employees to regularly update their skills. This could involve providing access to online learning platforms, sponsoring certifications, or offering internal training programs.
- Invest in Reskilling Programs: Support employees whose roles are affected by automation. Offer training that allows them to transition into new roles within the company.
- Implement Responsible Automation Frameworks: Focus on automating tasks, not entire jobs. Design automation strategies that improve employee productivity and job satisfaction, not just replace workers.
- Promote Transparency and Communication: Openly communicate automation plans with employees. Transparency builds trust and reduces anxieties about job displacement. This fosters collaboration and understanding.
Examples of Success: Indian Businesses Leading the Way
Many Indian companies are successfully navigating automation’s challenges and opportunities by investing in training programs, fostering continuous learning cultures, and implementing responsible automation frameworks.
- Infosys’s reskilling initiative: Infosys has invested heavily in reskilling its workforce, offering training in areas like AI, machine learning, and cloud computing. This empowers employees to take on new roles.
- Wipro’s digital academy: Wipro’s digital academy offers various training programs, helping employees adapt to the changing IT industry demands. This focus on skill development ensures employees remain valuable.
- Tata Consultancy Services’s focus on human-centric skills: TCS emphasizes human-centric skills, like creativity and problem-solving, alongside technical expertise. This balanced approach prepares employees for the future of work.
India has the potential to be a global leader in human-centered workforce automation. By taking a proactive and collaborative approach, individuals and organizations can ensure automation’s benefits are shared while minimizing negative consequences. Building a culture of continuous learning and adaptation is crucial for navigating this changing landscape.
Are you ready to navigate the changing dynamics of the Indian job market? Taggd specializes in Recruitment Process Outsourcing, helping organizations find the right talent. Visit Taggd.in to learn more about how we can support your workforce transformation.
